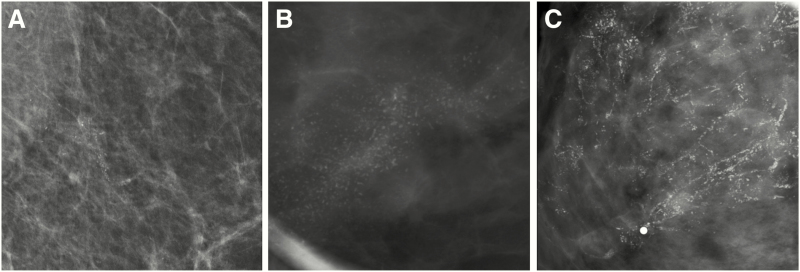
Figure 4.
Examples of various mammographic presentations of high nuclear grade DCIS, including asymptomatic linearly distributed amorphous calcifications on mediolateral 90-degree spot-magnification view (A), asymptomatic segmentally distributed fine pleomorphic calcifications on craniocaudal spot-magnification view (B), and diffusely distributed fine linear branching calcifications on craniocaudal spot-magnification view involving a clinically palpable, imaging occult mass (C). Microinvasion was present in both (A) and (C) on final surgical excision. Core needle biopsy (CNB)–diagnosed DCIS upgrades to invasive disease on surgical excision in approximately one quarter of cases. Risk factors for upgrade include clinical symptoms, mass on ultrasound or mammography, larger span, high nuclear grade, and CNB performed with a smaller gauge biopsy device.