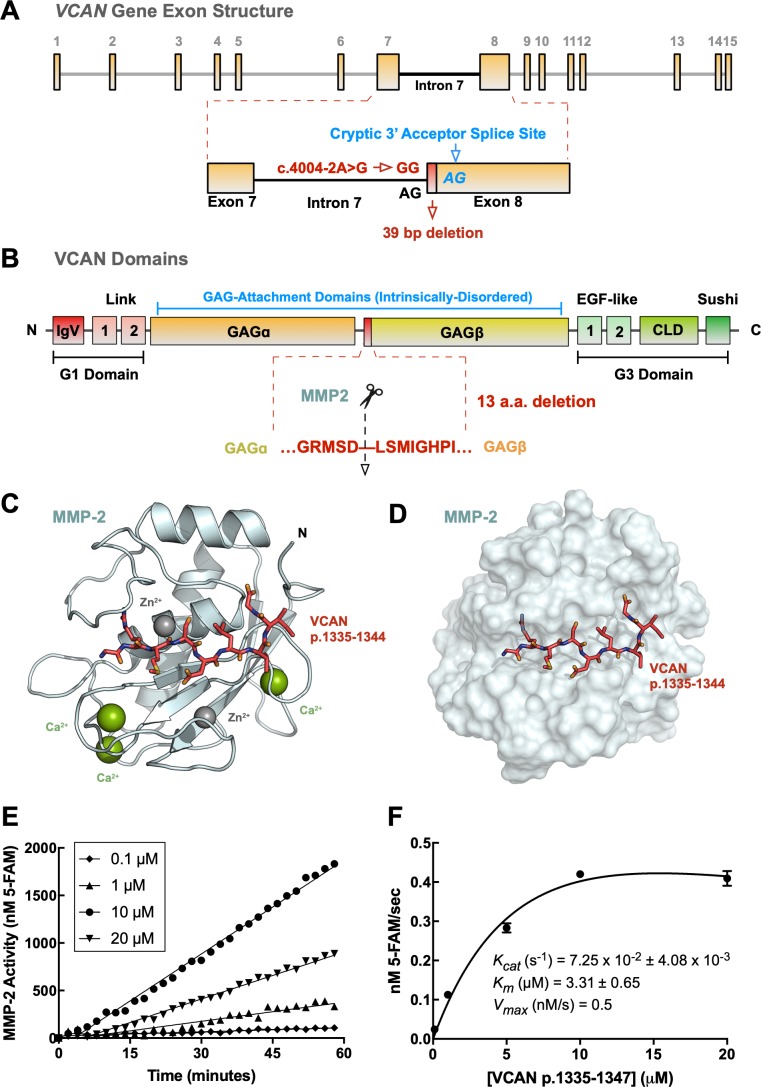
Figure 5.
MMP-2 cleaves the p.1335-1347 region of versican. Graphic representation of human VCAN gene exon structure showing location of the c.4004-2A>G splice site mutation in intron 7. The c.4004-2A>G creates a cryptic splice acceptor site 39-bp into exon 8 (A). Graphic representation of human versican domains (B). The VCAN p.1335-1347 region is deleted by the splice variant c.4004-2 A>G. This region corresponds to a putative MMP-2 cleavage site predicted by CleavPredict. In silico docking of VCAN p.1335-1344 to the MMP-2 catalytic domain structure (PDB: 1QIB) yielded a ΔG of 6.33 ± 0.28 kcal/mol across 25 runs in AutoDock VINA (C). Surface representation of the VCAN p.1335-1344-MMP-2 complex (D). Recombinant MMP-2 proteolytic activity was measured by cleavage of a FRET-tagged substrate (VCAN p.1335-1347; 5-FAM-GRMSDLSMIGHPI-QXL; Supplementary Table S3). Results are displayed as nanomolar product formed per minute time (E). Varying concentrations of substrate (to 20 μM) were added to calculate kinetic parameters. The initial velocity (nM 5-FAM/s) of the reaction at each substrate concentration was fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation and kinetic parameters were calculated: Kcat = 7.25 × 10−2 ± 4.08 × 10−3 s−1, Km = 3.31 ± 0.65 μM, Vmax = 0.5 nM/s (F).