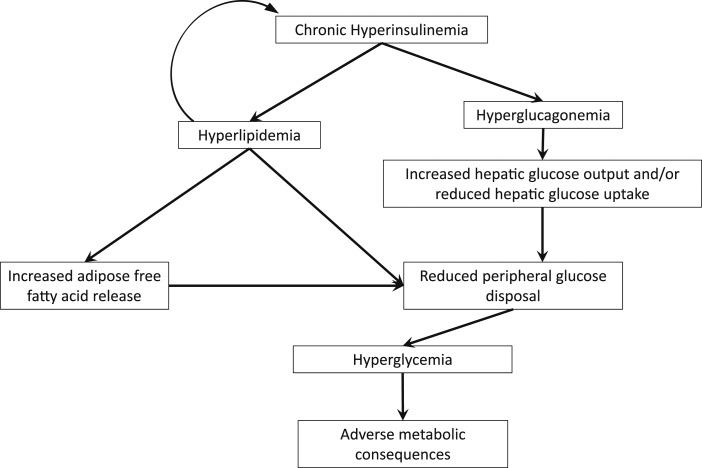
Figure 2.
Diagram of potential mechanisms for hyperinsulinemia with altered insulin pulsatility to induce metabolic disease. Chronic hyperinsulinemia of any potential etiology is associated with chronic hyperglucagonemia, which may lead to increased hepatic glucose output. Nutrient excess and hyperlipidemia contribute to adipose tissue expansion and dysfunction with eventual ectopic lipid deposition, which is associated with reduced muscle glucose disposal.