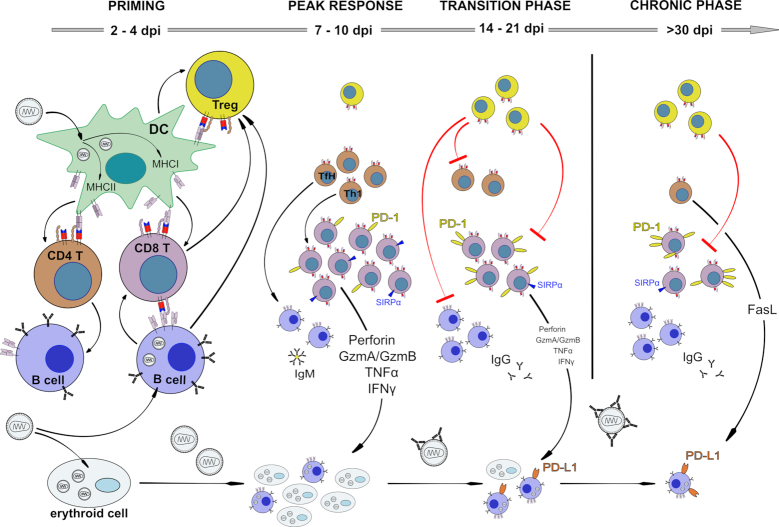
Figure 2.
Kinetics of adaptive immune responses during FV infection. Virus-infected DCs and B cells prime CD4+ and CD8+ effector T cells, but infected DCs can also initiate Treg responses. Membrane-bound TNFα-positive CD8+ T cells and GITR expressing B cells expand Tregs. Effector T cells as well as antibody-producing B cells control acute virus replication in a complex immune response. Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells are especially effective in restricting virus spread, but become exhausted via Tregs and inhibitory receptors during the transition phase between acute and chronic infection. Infected B cells upregulate ligands for inhibitory receptors and subsequently escape from CTL killing, suppress CD8+ T cell functions and form a persisting viral reservoir. During chronic infection most CD8+ T cells, except a few SIRPα-positive ones, are dysfunctional and virus replication is kept in check by cytotoxic CD4+ T cells and most likely neutralizing antibodies.