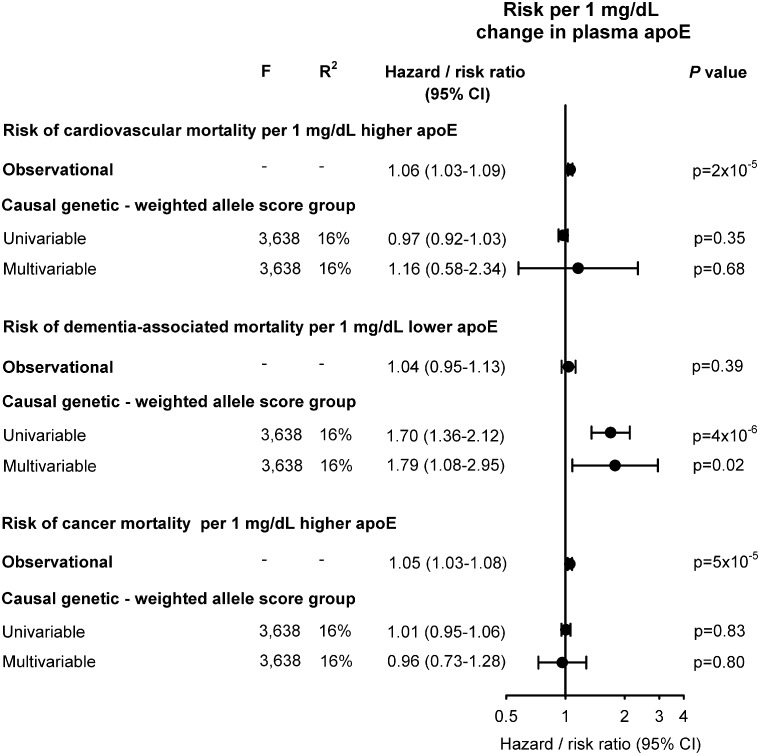
Figure 6.
Risk of cause-specific mortality for a 1 mg/dL change in observational and causal, genetically determined plasma apolipoprotein E level. The hazard ratio for a 1 mg/dL change in observational plasma apoE was calculated using Cox regression with adjustment for age (time scale), body mass index, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, lipid-lowering therapy, alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, education, postmenopausal status, hormonal replacement therapy, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, plasma triglycerides, and APOE genotype, whereas the corresponding risk ratios for the genetic change in plasma apoE for the weighted allele score was derived from univariable and multivariable instrumental variable analyses, including LDL cholesterol and triglycerides in multivariable analyses. A total of 74 560 individuals are included in these analyses. apoE, apolipoprotein E; CI, confidence interval; F, strength of the genetic instrument (>10 indicates sufficient statistical strength); P-value, significance of hazard ratios or risk ratios; R2, percent contribution of genetic instrument to the variation in plasma apoE.