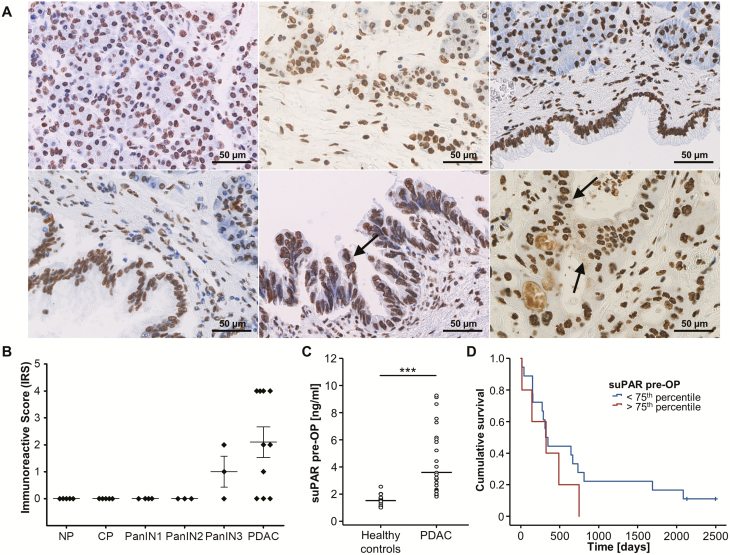
Figure 1.
uPAR expression and circulating levels of suPAR in pancreatic cancer—exploratory analyses. (A) Representative uPAR expression as detected by immunohistochemistry in normal pancreas (NP, upper left panel), chronic pancreatitis (CP, upper middle panel), PanIN1 (upper right panel), PanIN2 (lower left panel), PanIN3 (lower middle panel), and PDAC (lower right panel, all 400-fold magnification). Only PDAC and PanIN3 cells revealed small uPAR-positive intracytoplasmic speckles (black arrow) while a likely unspecific nuclear staining was present in all samples analyzed. Noteworthy, PDAC cells seem to secrete uPAR as indicated by positive staining of intraductular mucoid material in PDAC glands only. (B) Quantification of cytoplasmic uPAR expression according to the immunoreactive score (IRS) in NP, CP, PanIN, and PDAC samples. (C) Circulating levels of suPAR are significantly elevated in the exploratory cohort of PDAC patients (n = 23) when compared to healthy controls (n = 10). (D) Kaplan-Meier curve analysis shows a trend towards a reduced overall survival in patients with high suPAR levels (above the 75th percentile).