Figure 3.
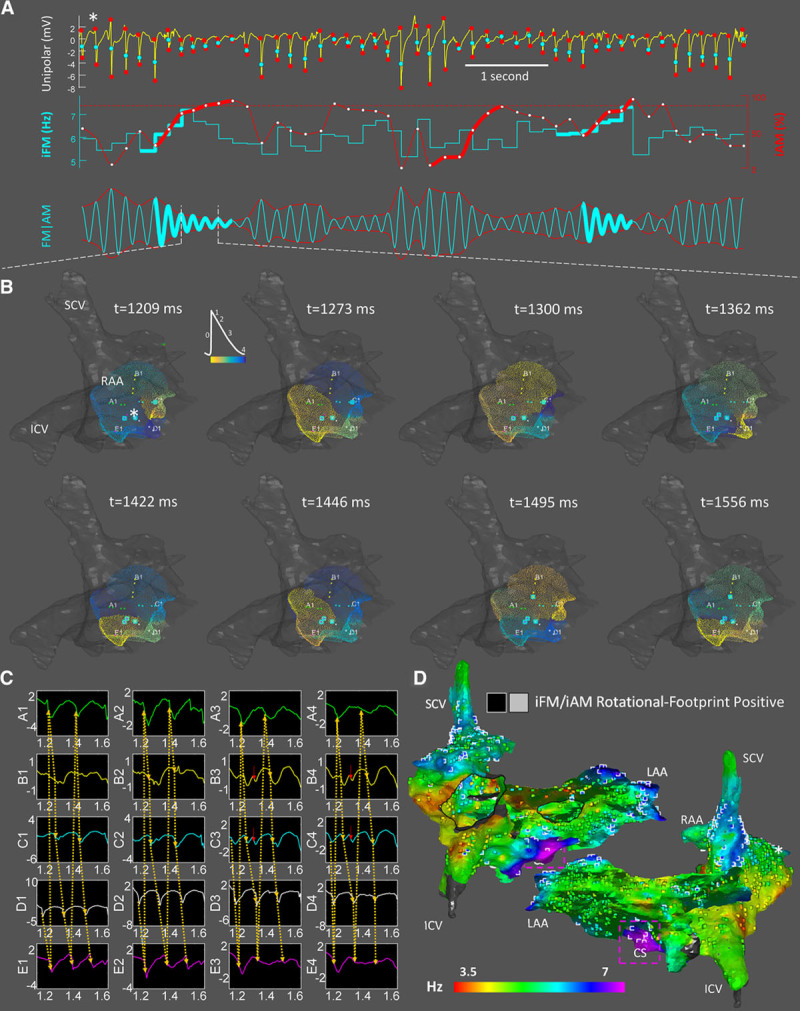
In vivo instantaneous frequency modulation (iFM)/ instantaneous amplitude modulation (iAM) calculation and single-signal rotational-footprint detection from unipolar electrical signals. A, Activation times (first row, cyan points) and unipolar amplitude excursions between the starts and ends of negative deflections (first row, red points) were used to generate the iFM (second row, cyan tracing) and the iAM (second row, red tracing) signals, respectively. Amplitude excursions simultaneous with ventricular activations were interpolated from the surrounding excursions because ventricular far-field residues may affect them, even after applying QRS minimization strategies. Time intervals with sustained simultaneously increasing iFM (thick cyan) and iAM (thick red) reaching a prespecified iAM threshold (dotted horizontal red line) are detected. Afterward, the rotor is still considered to be around while iAM keeps over the threshold and regardless of iFM. The third row displays a synthetic FM | AM signal (morphologically similar to an optical signal) that incorporated both iFM and iAM dynamic changes. Rotational-footprint positive intervals are highlighted. B, Snapshots from the phase movie obtained by interpolating data from the 20 electrodes of a PentaRay catheter fully deployed in the right atrial appendage (RAA; Online Movie III). Electrode locations with rotational-footprint positive signals are highlighted with cyan squares. Note the high correlation between highlighted electrodes and the center of rotation in the phase movie. See also Online Movie IV from left atrial appendage (LAA). C, Unipolar electrograms confirming the reentrant activation displayed in B. Red arrows mark depolarizations that may be explained by precession of the rotational core (Online Figure/Movie II). D, Combined leading-driver (iFMmedian) + rotational-footprint map. Rotational-footprint positive locations are marked with black/white squares within light/dark areas, respectively. Interestingly, many regions displayed repetitive rotational activations, including the RAA and LAA. However, most of them did not seem hierarchically relevant to drive AF since it acutely terminated and was rendered nonsustainable after ablating only the purple area located in the coronary sinus. Importantly, rotational-footprints were also found in that region. *The location from which the signal in A was retrieved. ICV indicates inferior cava vein; and SCV, superior cava vein.
