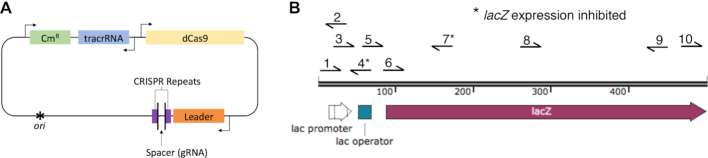
Figure 1.
Plasmid pdCas9 and the chromosomal lacZ target. (A) Plasmid pdCas9 (37) encodes a catalytically inactive Cas9 variant (dCas9) in which the nuclease activity is abolished by the D10A and H840A mutations. Expression is driven by the strong native Cas9 promoter from Streptococcus pyogenes. The spacer is the user-defined sequence that base pairs with the target site. (B) The target site for dCas9 binding was the Escherichia coli lacZ gene. Ten candidate spacers were selected to target the promoter and early open reading frame of lacZ. Of these 10 candidates, only spacers 4 and 7 inhibited transcription completely, as judged by a white colony on X-gal indicator plates.