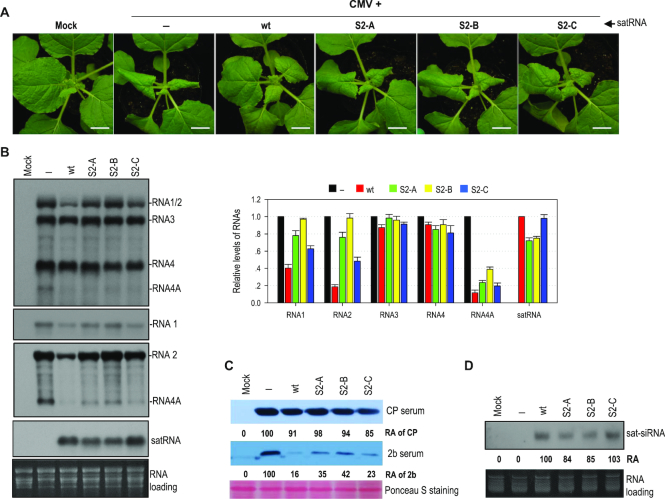
Figure 9.
The γH2 hairpin engaged in the inhibition of the accumulation of CMV RNAs by sat-T1. (A) Disease symptoms in Nicotiana benthamiana plants infected with CMV alone (–) or plus sat-T1 wild-type (wt) or γH2 mutants as indicated on the top. These mutants have been depicted in Figure 8. The plants were photographed at 6 days post-infiltration (dpi). Mock plants were infiltrated with infiltration solution. Bar: 1 cm. (B) Accumulation of CMV, sat-T1 and its mutants in the infected plants analyzed by northern blot hybridization. Total RNAs were extracted from the upper systemic leaves at 6 dpi. The DNA oligonucleotide probes targeting CMV 3′ UTR, 1a and 2b were used to detect all viral RNAs, RNA1, and RNA2 and its subgenomic RNA4A, respectively. The signal intensities of CMV and satellite RNAs were arbitrarily quantified using the program Gel Pro Analyzer 4.0. The relative level of each RNA species is shown in the chart on the right. All of viral RNAs in the CMV-infected plants were assigned a value of 1, as well as wt sat-T1. The columns represent the averaged value and standard error from three independent biological experiments. The ethidium bromide-stained rRNAs were used as a loading control. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the accumulation of the CMV CP and 2b proteins in the infected plants. Total proteins were prepared from the upper systemic leaves at 6 dpi, and separated in a SDS-contained polyacrylamide gel for immunoblotting using antiserum against CMV CP or 2b. The values represent relative accumulation levels. (D) Northern blot hybridization analysis of the accumulation of satRNA-derived siRNAs (sat-siRNAs) in the upper systemic leaves at 6 dpi. The signal intensities of sat-siRNAs were arbitrarily quantified using the program Gel Pro Analyzer 4.0. The numbers shown below represent the relative accumulation level of sat-siRNAs.