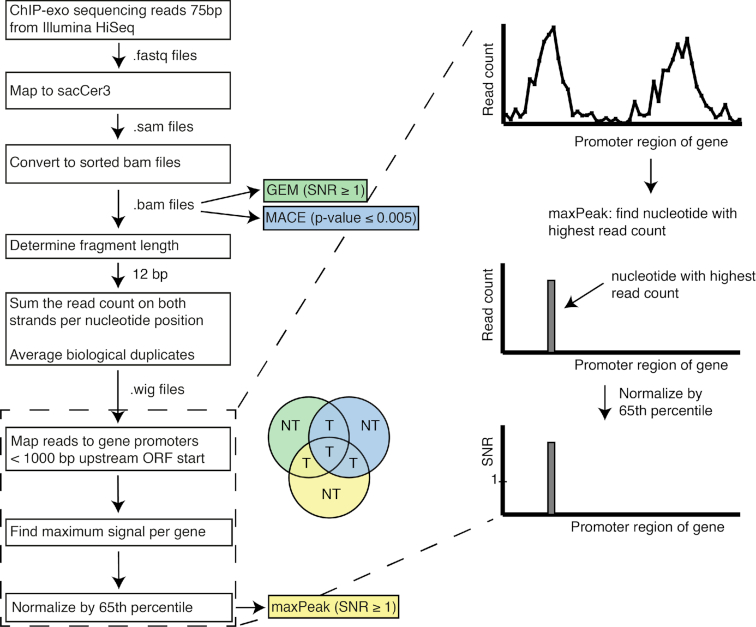
Figure 2.
Illustration of the pipeline implemented for the identification of target genes from ChIP-exo data. First, BAM files were generated, sorted and indexed, on which GEM and MACE are run. For the maxPeak peak detection method, the number of reads on both DNA strands for each nucleotide is counted and, subsequently, the highest read count at a single nucleotide per gene is assigned as the gene’s signal. Finally, the read count for each gene is normalized by the 65th percentile of all genes with a read count > 0, calculating a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Finally, target genes (indicated by a ‘T’ in the pie chart) are selected if these are retrieved as significant by at least two out of three peak detection methods (PDMs); conversely, target genes that are retrieved as significant by only one PDM (indicated as ‘NT’ in the pie chart) are not considered further in the analyses.