Figure 1.
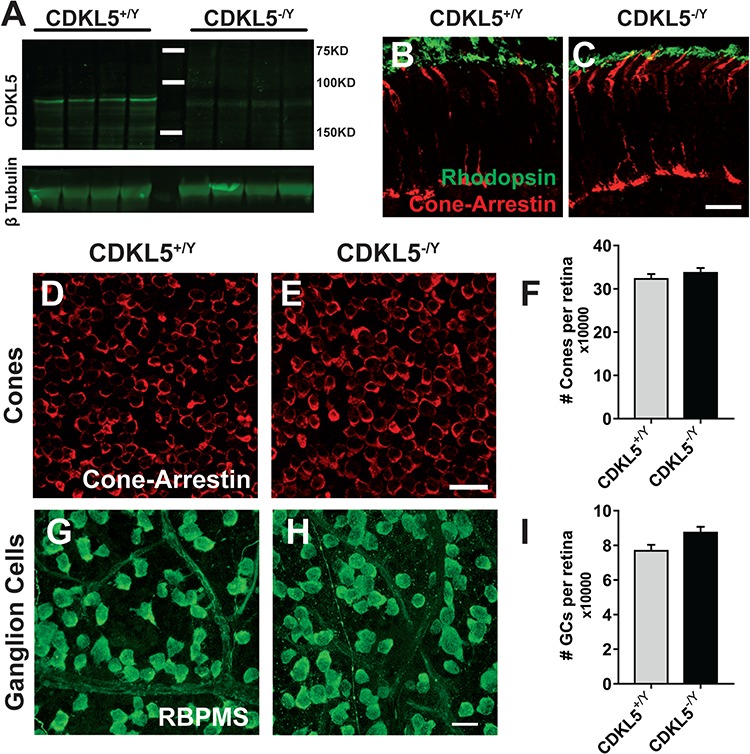
CDKL5 null mice show normal retinal morphology. (A) Western blot analysis on adult male CDKL5−/y and WT (CDKL5+/y) retinal homogenates showing CDKL5 expression. (B and C) Retinal sections stained for cone photoreceptors (cone arrestin, red) and rod outer segments (rhodopsin, green). The overall structural organization of photoreceptor cells is identical in the two experimental groups. (D and E) Representative images from retinal whole-mount preparations of CDKL5+/y (D) and CDKL5−/y (E) stained for cone arrestin as a cone marker. (F) Quantitation of the total number of cones showed no statistical significance between the two groups (two-tailed Student’s t-test P = 0.435). (G and H) Representative images from retinal whole-mount preparations of CDKL5+/y (G) and CDKL5−/y (H) stained for RBPMS as a RGCs marker. (I) Quantitation of the total number of cones (I) showed no statistical significance between the two groups (two-tailed Student’s t-test P = 0.098). Scale bars are equal to 20 μm. Error bars represent standard error of mean (SEM).
