Figure 4.
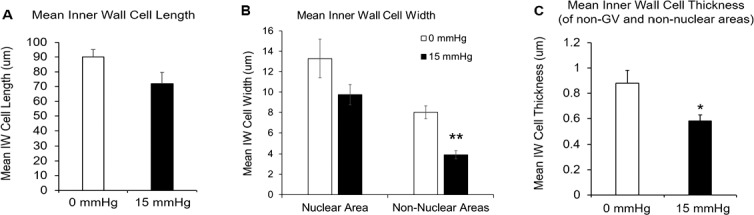
Comparison of cell length, width, and thickness between immersion-fixed group (0 mm Hg, n = 12 cells) and perfusion-fixed group (15 mm Hg, n = 12 cells). (A) The mean cell length of IW cells from perfusion-fixed eyes was shorter than those from immersion-fixed eyes (71.88 ± 7.74 μm vs. 90.21 ± 5.00 μm; P = 0.06), but the difference did not reach significance. (B) The mean cell width of IW cells at the nuclear area from perfusion-fixed eyes was slightly narrower than those from immersion-fixed eyes (9.74 ± 1.00 μm vs.13.29 ± 1.89 μm), but the difference did not reach significance (P = 0.11). The mean cell width in non-nuclear areas was significantly narrower in perfusion-fixed eyes (3.90 ± 0.41 μm) than immersion-fixed eyes (8.01 ± 0.63 μm; P < 0.001). (C) The mean cell thickness of non-GV and non-nuclear regions was significantly thinner in perfusion-fixed eyes than in immersion-fixed eyes (0.58 ± 0.05 μm vs. 0.88 ± 0.01 μm; P = 0.02). Error bars: SEM. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01.
