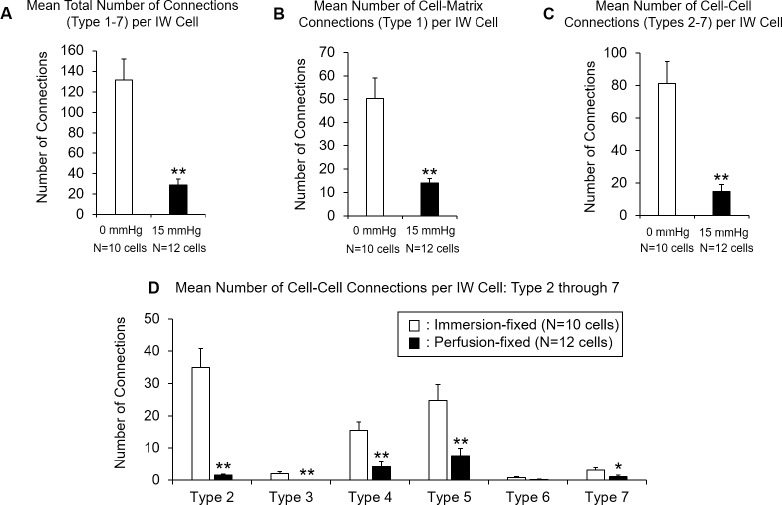
Figure 6.
Comparison of mean number of connections in each IW cell to underlying JCT cells/ECM between perfusion-fixed (n = 12 cells) and immersion-fixed (n = 10 cells) eyes. (A) Mean total number of IW/JCT connections (sum of type 1-type 7) was significantly reduced in perfusion-fixed eyes (29 ± 6 connections), compared to immersion-fixed eyes (132 ± 20 connections; P = 0.0001). (B) Mean number of cell-to-ECM connections (type 1 only) between each IW cell with underlying JCT ECM was significantly reduced in perfusion-fixed eyes (14 ± 2 connections), compared to immersion-fixed eyes (50 ± 9 connections; P = 0.0002). (C) Mean number of cell-to-cell connections (types 2–7 altogether) between each IW cell with JCT cell bodies was significantly reduced in perfusion-fixed eyes (15 ± 4 connections), compared to immersion-fixed eyes (81 ± 13 connections; P = 0.0001). (D) Mean numbers of six different types of cell-to-cell connections between each IW cell and JCT cells are shown. All but type 6 connections were significantly reduced in perfusion-fixed eyes, compared to immersion-fixed eyes (P < 0.01). Error bars: SEM. *P ≤ 0.05; **P < 0.01.