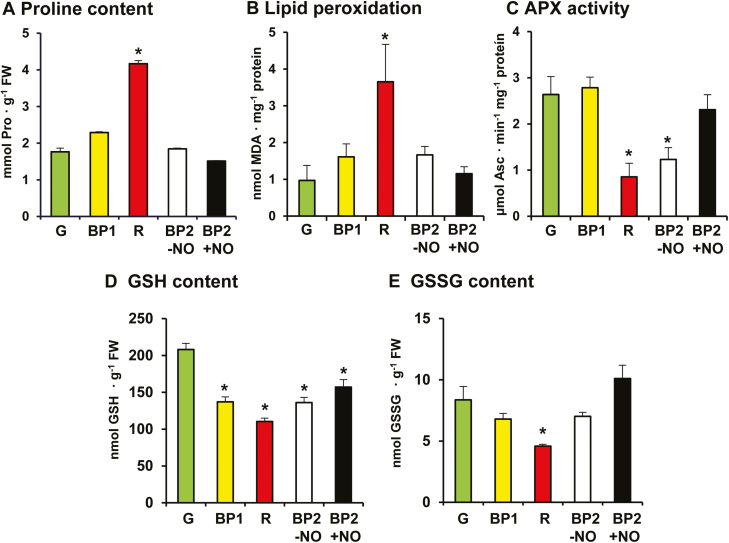
Fig. 5.
(A) Proline content, (B) lipid peroxidation level, (C) ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity, (D) reduced glutathione (GSH) content, and (E) oxidized glutathione (GSSG) contents of sweet pepper fruits at different stages of ripening: immature green (G), breaking point 1 (BP1), breaking point 2 with and without NO treatment (BP2+NO and BP2–NO, respectively), and ripe red (R). Lipid peroxidation was determined by the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances method, using malondialdehyde as standard. Pairwise analysis of variance was used to detect differences in comparison to green fruits. *P<0.05. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)