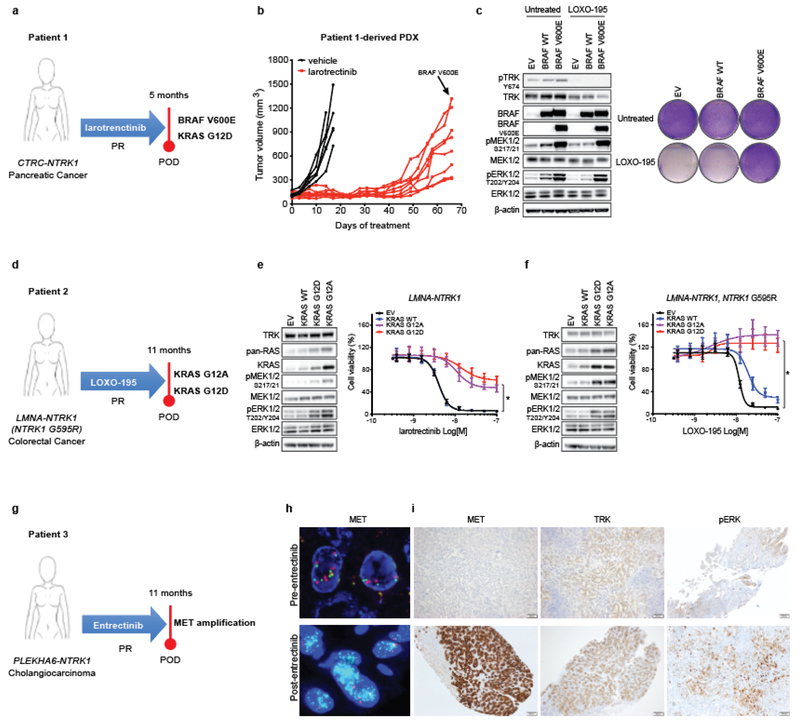
Fig. 1: Alterations in the MAPK pathway or an upstream receptor tyrosine kinase confer resistance to TRK inhibitors in patients and preclinical models.
a, Schematic showing acquired BRAF V600E and KRAS G12D mutations in a CTRC-NTRK1-positive pancreatic adenocarcinoma patient with acquired resistance to the first-generation TRK inhibitor, larotrectinib. b, Tumor growth of larotrectinib-sensitive patient-derived xenografts established from this patient’s tumor treated with larotrectinib (200mg/Kg, 5 days/week). Genotyping at the time of acquired resistance identified outgrowth of a BRAF V600E-positive clone. c, Western blot and cell viability assay of a TPR-NTRK1, NTRK1 G595R pancreatic cancer cell line with ectopic expression of BRAF V600E and treated with 50nM of LOXO-195 for 24 (WB) or 72 (cell viability) hours. Total and phosphorylated proteins detected are indicated. Two biological replicates were performed for each experiment. d, Schematic showing presence of KRAS G12A and G12D mutations in a LMNA-NTRK1 fusion-positive colorectal cancer patient with acquired resistance to LOXO-195. Note that KRAS G12D emerged in cfDNA upon further disease progression (17 months on LOXO-195 therapy). e, f, Western blot for MAPK effectors and cell proliferation curves of a LMNA-NTRK1 (e) and a LMNA-NTRK1, NTRK1 G595R (f) colorectal cancer cell lines with ectopic expression of KRAS G12A and G12D, treated as indicated. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was used to evaluate significant differences in % of viable cells. * indicates differences that were considered statistically significant (P<0.05). Exact P values are P=0.000000000000001 for the LMNA-NTRK1 cell line and P=0.000000001115265 for the LMNA-NTRK1, NTRK1 G595R cell line. Two biological replicates were performed for each experiment. g, Schematic showing acquired MET amplification in a PLEKHA6-NTRK1 fusion-positive cholangiocarcinoma patient with acquired resistance to entrectinib. h, Representative fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and i, Immunohistochemistry (IHC) images of the pre- and post-entrectinib tumor biopsies from this patient. Lower panels show confirmed acquisition of MET amplification in the post-entrectinib sample (h) and increased MET and pERK staining by IHC (i). FISH and IHC were performed two independent times and similar results were obtained.