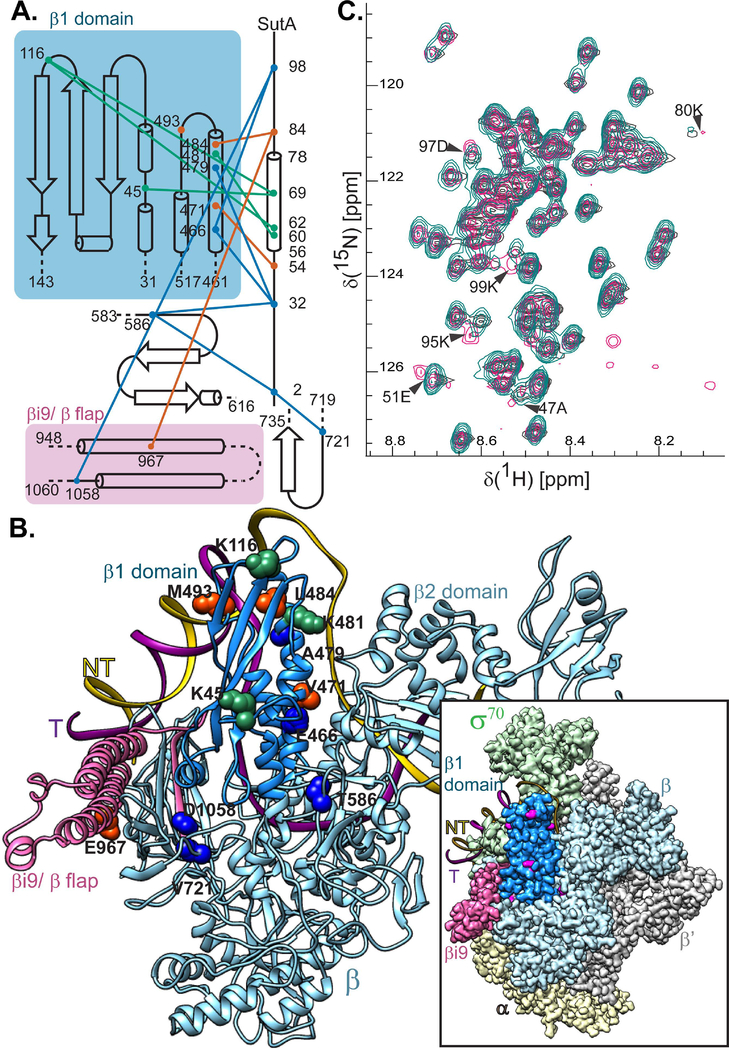
Figure 2. SutA interacts with the β subunit of RNAP.
A. A topology diagram of the contacts inferred by cross-linking (BS3, green lines; BPA, orange lines) and FeBABE-mediated cleavage (blue lines). Cross-linked residues were identified by LC-MS/MS and cleavage sites were determined by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting of the cleaved complexes, using a large-format gel system and Abcam antibody EPR18704, against the extreme C-terminus of the E. coli β. Cross-linking and cleavage reactions were performed using the core RNAP. See text and Extended Experimental Procedures for further details. B. Residues involved in cross-links or cleavages were mapped onto a structure generated by threading the P. aeruginosa sequence onto a crystal structure of the E. coli β subunit (PDB:5UAG). The relative position of the DNA in a crystal structure of the E. coli Eσ70 open complex is shown for reference. Inset shows the cryo-EM structure of E. coli Eσ70 (PDB: 6CA0), but with the P. aeruginosa sequence threaded model of the β subunit substituted in. Cross-linking and cleavage residues that are visible in this view (K45, K116, K481, M493, T586, and V721) are indicated in magenta for maximum contrast. The darker blue color indicates the positions of the β1 domain (the fragment purified for (C)) and pink indicates the βi9/β flap region that is shown in (A). C. 1H-15N HSQC spectra showing that chemical shifts for a handful of residues are perturbed when 15N-labeled SutA is mixed with unlabeled β1 domain (magenta) vs when it is analyzed alone (turquoise) or mixed with unlabeled σS (dark grey). A small number of background peaks show up only in the β1 domain mixture (magenta, lower right quadrant); these are most likely due to the fact that the protein concentration was lower in this sample.