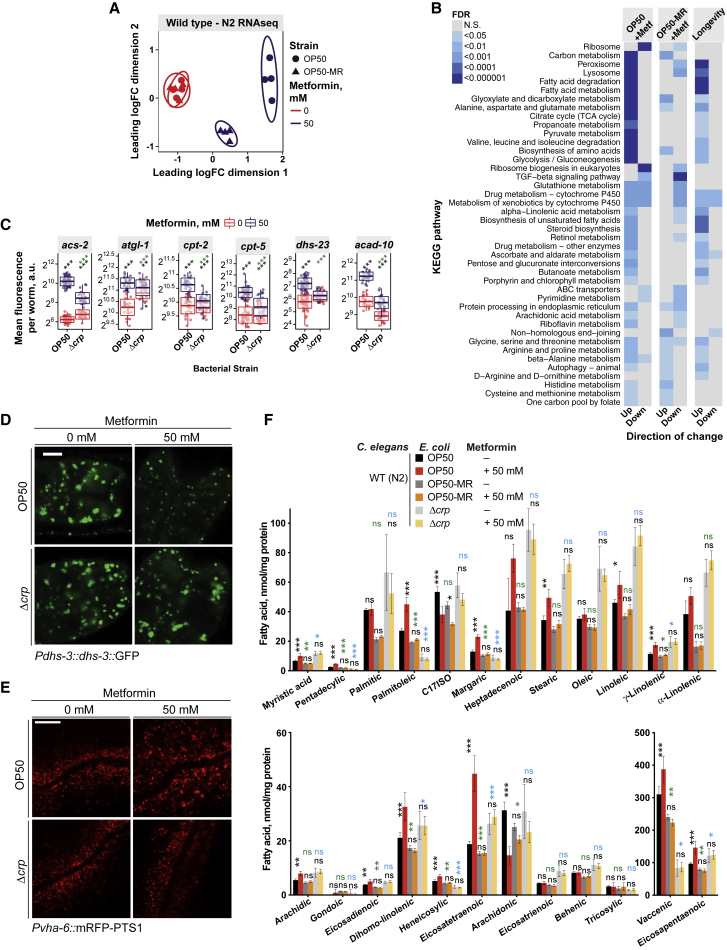
Figure 6.
Metformin and Bacterium-Dependent Transcriptional and Metabolic Signatures in C. elegans
(A) Multi-dimensional scaling plot of worm RNA-seq data showing distinct and bacterium-dependent transcriptional signatures associated with metformin treatment.
(B) KEGG pathway enrichment for worm RNA-seq data.
(C) Metformin increases expression of worm lipid-related genes in a bacterium-dependent manner as effects are suppressed in OP50 Δcrp. Similar effects were observed for worms grown on OP50-MR (Figures S6B and S6C).
(D and E) Confocal visualization of worm lipid droplets (D) and peroxisomes (E), showing effects of metformin in worms in a bacterial Crp-dependent manner. Similar effects were observed for worms grown on OP50-MR (Figures S6E and S6F). Scale bars, 10 μm. No changes in gene expression for dhs-3 or vha-6 were observed (Table S6).
(F) Metabolomics in worms show an interaction between metformin and bacteria on host fatty acid profiles.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. In (E) and (F), significance stars represent metformin effect (black) and metformin-bacterium interaction (green or blue).
See also Table S6 for RNA-seq statistics and Table S7 for fatty acid metabolomics statistics.