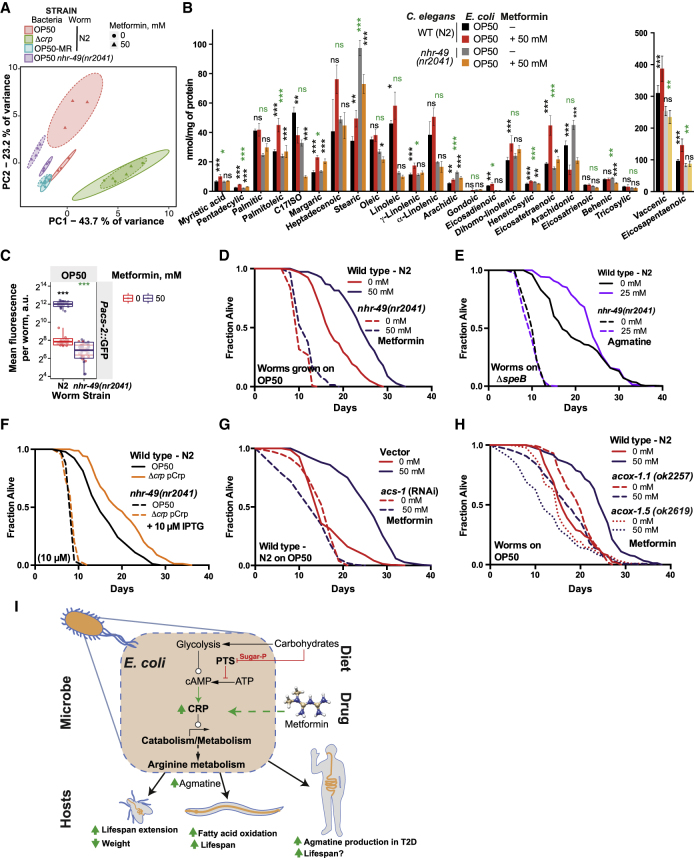
Figure 7.
Metformin Increases Fatty Acid Oxidation to Regulate Host Metabolism and Lifespan
(A) PCA plot of fatty acid metabolomics data, showing distinct signatures of metformin in worms in a bacterium- and worm nhr-49-dependent manner.
(B) Fatty acid metabolomics in worms, showing an interaction between metformin and worm nhr-49.
(C–F) Host nhr-49 regulates metformin effects on worm Pacs-2::GFP expression (C) and the effects of metformin (D), agmatine supplementation (E), and E. coli OP50 Crp overexpression (F) on the worm lifespan.
(G and H) Worm lifespan extension by metformin is abolished by RNAi knockdown of the mitochondrial FAO gene acs-1 (G) and in acox-1.1 and acox-1.5 peroxisomal FAO mutants (H).
(I) Proposed model of host-microbe-drug-nutrient interactions that regulate metformin effects on host metabolism and lifespan.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. In (B) and (C), significance stars represent metformin effect (black) and metformin-genotype interaction (green).
See also Table S1 for lifespan statistics and Table S7 for fatty acid metabolomics statistics.