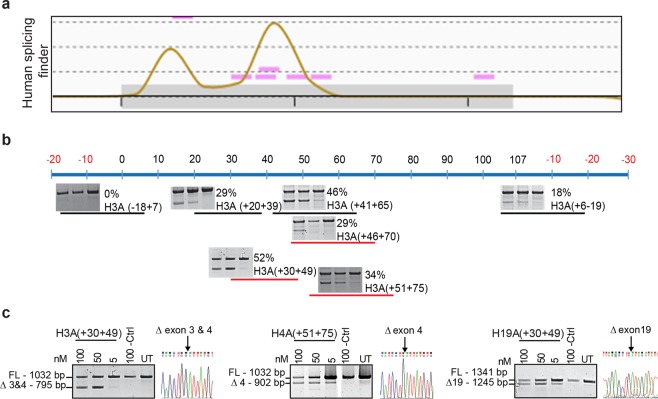
Figure 1.
Design and experimental evaluation of ITGA4-targeting AOs. AOs designed to induce exon 3 skipping of the ITGA4 transcript are shown. (a) Splice enhancer motifs predicted by the Human splicing finder tool for exon 3 (grey box) and partial intron 2 and 3 (solid black lines outside the grey box). The height of the peaks represents the collective strength of the motifs. Purple bars show the location and strength of each predicted motif. (b) AO designed for exon 3 based on the analysis in (a). The negative numbers in red indicate the nucleotide positions of the intron relative to exon and the numbers in black represent the nucleotide positions of the exon relative to the acceptor site. Short black lines represent AOs designed for initial screen that cover the sequences around the peaks, acceptor and donor sites. The short red lines represent microwalking AOs designed to refine AO H3A(+41 +65) to achieve maximum exon skipping efficiency with minimal AO length. Only selective microwalking AOs for H3A(+41 +65) are shown as examples for illustration. Gel fractionation of RT-PCR products of ITGA4 amplicons from healthy fibroblasts transfected with 2OMe PS AOs at various concentrations (100, 50 and 5 nM from left to right) for 24 hr is shown above each AO. The percentage of exon skipping determined as described in Materials and Methods and the AO names are also shown. (c) The top three AOs for exon 3, 4 and 19 selected after microwalking to perform further studies. RT-PCR products of ITGA4 amplicons from healthy fibroblasts after transfection with the corresponding 2OMe PS AOs at indicated dosages for 24 hr and confirmation of exon skipping by Sanger sequencing are shown. Ctrl: control AO, UT: untreated. The gels were cropped for presentation and full-size gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. S5.