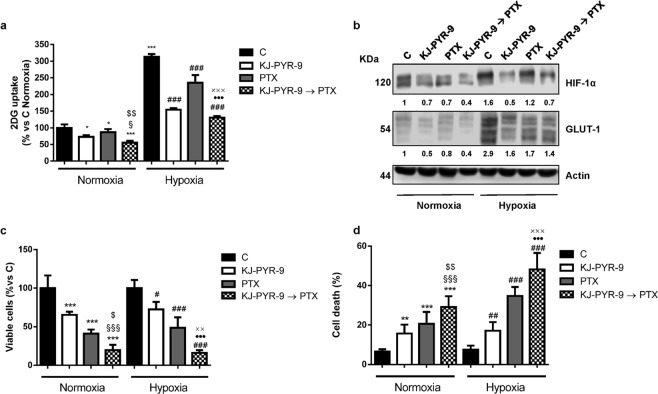
Figure 6.
Inhibition of c-myc activity affects glucose metabolism in TNBC cells under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated for 48 h with 20 µM KJ-PYR-9 and 10 nM paclitaxel alone or treated with KJ-PYR-9 for 24 h and then with paclitaxel for further 24 h (KJ-PYR-9 → PTX) in normoxic or hypoxic (1% O2) conditions. Glucose uptake (a) was measured. b The expression of the indicated proteins was analyzed by Western blotting. The immunoreactive spots were quantified by densitometric analysis, and HIF-1α/Actin and GLUT-1/Actin ratios were calculated; the data are expressed as fold increase versus control (control value = 1). Cell viability (c) and cell death (d) were assessed by counting the cells in a Bürker hemocytometer with the trypan blue exclusion method and by fluorescence microscopy after Hoechst 33342/PI staining, respectively. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs C Normoxia (N); §p < 0.05, §§§p < 0.001 vs KJ-PYR-9 N; $p < 0.05, $$p < 0.01, $$$p < 0.001 vs PTX N; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs C Hypoxia (H); ●●●p < 0.001 vs KJ-PYR-9 H; xxp < 0.01, xxxp < 0.001 vs PTX H. Data in (a,c,d) are mean values ± SD of three independent experiments. Results in (b) are representative of two independent experiments.