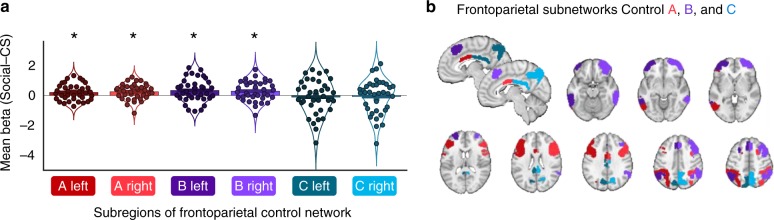
Fig. 4.
Difference between Social and CS effects in frontoparietal control subnetworks. a Difference in mean path a beta weight (Social–CS) in Control A (dark and bright red), Control B (dark and bright purple), and Control C (dark and bright blue) subnetworks in the left and right hemisphere (dark and bright colors, respectively). Each dot reflects the difference in mean beta estimates of one participant. Significantly greater activation for social information was found in the Control A (left: t(35) = 2.3, p = 0.027, 95% CI = [0.03, 0.39], Cohen’s d = 0.38; right: t(35) = 2.9, p = 0.006, 95% CI = [0.08, 0.43], Cohen’s d = 0.48) and the Control B (left: t(35) = 2.6, p = 0.012, 95% CI = [0.08, 0.59], Cohen’s d = 0.44; right: t(35) = 2.6, p = 0.013, 95% CI = [0.07, 0.51], Cohen’s d = 0.44), but not in the Control C network. Asterisks denote networks with significant differences between social information and CS effects (using t-tests, p < 0.05). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b Display of frontoparietal control subnetworks A (dark and bright red), B (dark and bright purple), and C (dark and bright blue) on sagittal and transversal brain slices