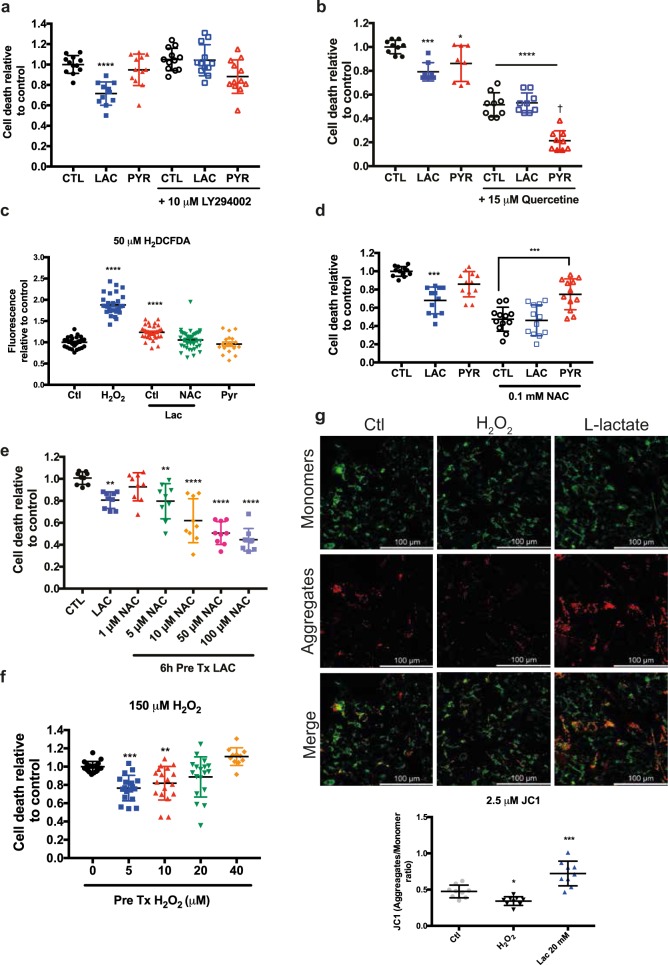
Fig. 3. PI3K and UPRER pathways mediate lactate-mediated cell survival through ROS production.
a Relative cell death assessed by trypan blue exclusion following oxidative stress induced by 150 μM H2O2. Prior to oxidative stress exposure, SH-SY5Y cells were co-treated for 6 h with 10 μM LY2940002 and lactate or pyruvate. b The measure of cell death after 150 μM H2O2 treatment upon pre-treatment with lactate and pyruvate. Cells were co-treated with UPRER inhibitor (Quercetine – 15 μM) with 20 mM lactate or pyruvate. c The measure of ROS level using H2DCFDA upon 150 μM H2O2, 20 mM lactate or pyruvate and 100 μM N-acetylcysteine. d Relative cell death measurements following oxidative stress induced by 150 μM H2O2. Prior to oxidative stress exposure, cells were co-treated for 6 h with 100 μM N-acetyl-cysteine lactate or pyruvate. e. Relative cell death measurements following oxidative stress induced by 150 μM H2O2. Prior to oxidative stress exposure, cells were co-treated for 6 h with increasing doses of N-acetyl-cysteine and 20 mM lactate. f Measure of cell death after 150 μM H2O2 and pre-treated with low doses of H2O2. g Confocal images of SH-SY5Y cells stained with JC1 (2.5 μM). Cells were treated with 150 μM H2O2 for 30 min or with 20 mM lactate for 6 h. (N = 4), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, †(p < 0.0001 compared to Quercetine treated ctl)