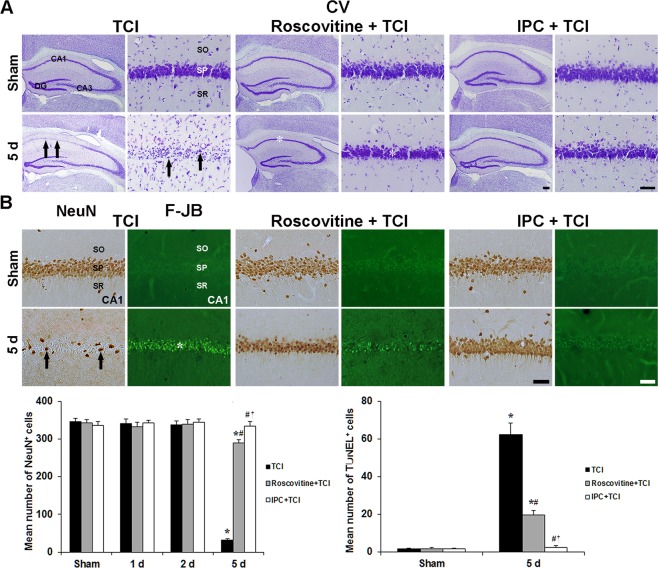
Figure 1.
Roscovitine- and IPC-mediated neuroprotection against TCI. (A) CV staining in the hippocampus of the TCI (1st and 2nd columns), roscovitine + TCI (3rd and 4th columns) and IPC + TCI (5th and 6th columns) groups. CV+ CA1 pyramidal neurons (arrows) are damaged 5 days after TCI; however, CV+ CA1 pyramidal neurons (asterisks) in the roscovitine + TCI and IPC + TCI groups are similar to those in the sham group. Scale bar = 800 µm (1st, 3rd and 5th columns), 50 µm (2nd, 4th and 6th columns). (B) NeuN immunohistochemistry (1st, 3rd and 5th columns) and F-J B histofluorescence staining (2nd, 4th and 6th columns) in the CA1 area of the TCI (1st and 2nd columns), roscovitine + TCI (3rd and 4th columns) and IPC + TCI (5th and 6th columns) groups. In the TCI group, a few NeuN+ (arrows) and many F-J B+ (asterisk) CA1 pyramidal neurons are detected 5 days after TCI. In the roscovitine + TCI and IPC + TCI groups, many NeuN+ pyramidal neurons are observed in the CA1 area; F-J B-positive cells are lower than those in the TCI group. SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. Scale bar = 50 µm. Quantitative graphs for numbers of NeuN+ (left) and F-J B+ (right) CA1 pyramidal neurons. The bars are reported as means ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 7, *P < 0.05 vs. sham group; #P < 0.05 vs TCI group; †P < 0.05 vs roscovitine + TCI group).