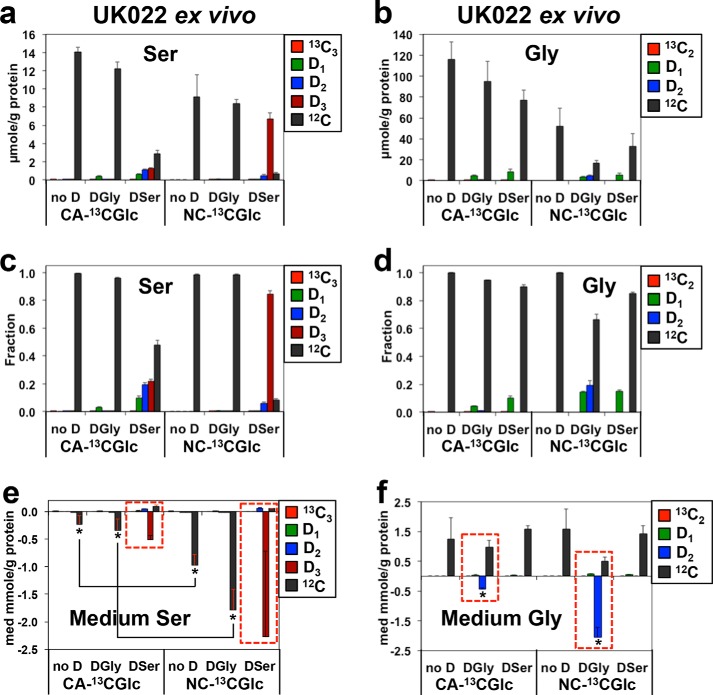
Figure 4.
Analysis of 13C and D isotopologues of Ser and Gly reveals reduced Ser/Gly uptake but enhanced Ser–Gly one-carbon exchanges in human CA versus matched NC lung tissues ex vivo. UK022 patient sample treatment, processing, extraction, and ECF derivatization were as described under “Experimental procedures.” The respective level (a and b) and fractional enrichment (c and d) in 13C and d isotopologues of Ser or Gly in tissues and uptake or release of these Ser or Gly species in the medium (e and f) were obtained from UHR-FTMS analysis, as described under “Experimental procedures.” D1, D2-Ser in a, c, and e and D1-Gly in b, d, and f represented D-scrambled Ser and Gly, respectively. no D, [13C6]Glc only; DSer, D3-Ser + [13C6]Glc; DGly, D2-Gly + [13C6]Glc. Using the two-tailed unpaired t test, the absolute levels of D1-, D2-, and D3-serine differed between CA versus NC tissues (n = 3 each) (a) 2-fold for D1 (p = 0.01, t = 4.472), 3-fold for D2 (p = 0.002, t = 70.7), and 0.27 for D3 (p = 0.0032, t = 6.31). The fractional enrichment differed for CA versus NC tissues with (c) 7-fold for D1 (p = 0.0042, t = 5.884), 3.5-fold for D2 (p = 0.001, t = 8.575), and 0.27-fold for D3 (p = 0.0001, t = 19.677). For D1- and D2-glycine, the fractional enrichments differed between CA versus NC tissues (d) 0.3-fold for D1 (p = 0.0001, t = 24.748) and 0.07-fold for D2 (p = 0.0029, t = 6.492). The absolute levels in b were too low for reliable statistical testing. Because of large standard errors, the difference (4.4-fold) in the uptake of D3-serine from the medium did not reach statistical significance between CA versus NC tissues (e), but the differential uptakes (4.2–5.2-fold) of unlabeled (12C) Ser between the two tissue types were statistically significant (*, p = 0.018, t = 4.695). The uptake of D2-Gly decreased 23-fold in CA versus NC tissues (f) (*, p = 0.02, t = 6.856).