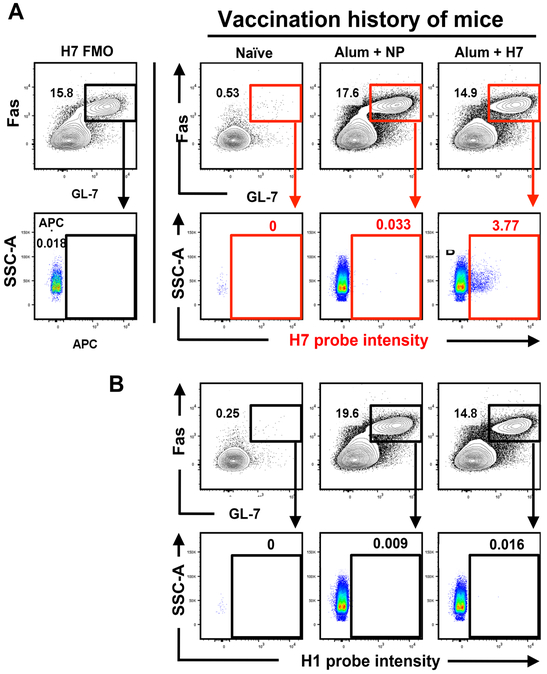
Figure 3. Fluorescent H7-probe specifically detects H7-speciic GC B cells, which are not detected by an H1 specific probe.
Mice were immunized subcutaneously in the footpad either with H7 protein or influenza nucleoprotein (NP) in alum. 14 days post-immunization, popliteal lymph nodes (pLN) were harvested and single cells analyzed by flow to detect H7-specific GC B cells. A) An APC-labeled H7- probe was used to identify H7-specific GC B cells. Representative staining is shown to illustrate the expression pattern of H7-specific GC B cells (CD4−CD19+B220hiCD138−GL−7+Fas+) in naïve mice, H7- immunized or NP-immunized mice as indicated in the top of the figures. H7 reactivity was only detected in the pLN from the H7 vaccinated mice. B) An APC-labeled H1-probe (A/California/04/09) was used in a separate aliquot of cells from the same cohorts of mice, showing the selectivity of binding.