Fig. 6.
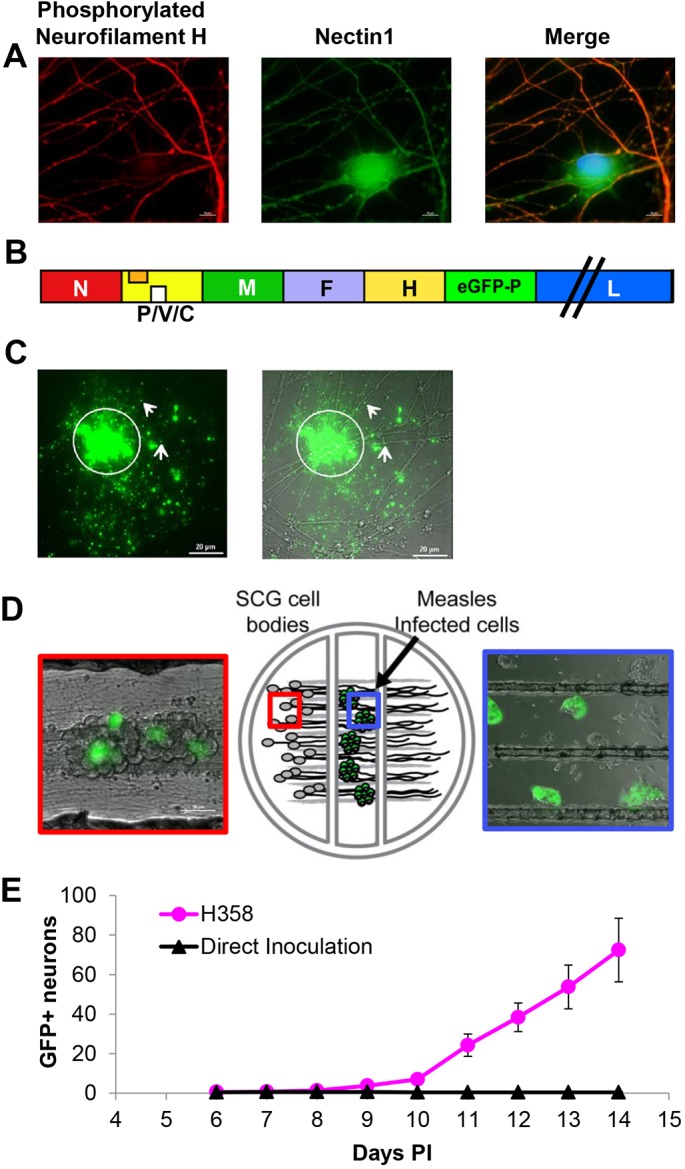
MeV spreads from infected epithelial cells to primary neurons. (A) Primary mouse SCG neurons stained with mouse monoclonal phosphorylated neurofilament H-specific antibody (red) or rabbit polyclonal N1-specific antibody (green). Nuclei are contrasted with Hoechst staining (blue). While phosphorylated neurofilament H is only present in axons, N1 is observed in all neuronal structures. (B) Schematic of the recombinant MeV-RNPtracker genome. The additional transcription unit expressing eGFP–P is inserted after the H gene. (C) Viral RNP in association with neuronal axons after co-culture with H358 cells infected with MeV-RNPtracker. Left: GFP fluorescence associated with the MeV-RNPtracker structures. Right: merged phase-contrast image. The arrows indicate GFP positivity distal to cell contact sites. (D) Center panel: drawing of the compartmentalized neuronal culture system. Dissociated mouse SCG neurons are plated in the left compartment. The neurons extend neurite projections underneath two sequential barriers into the right compartment. Right panel: cells infected with MeV-RNPtracker are plated onto the neurites in the middle compartment; the picture was taken 48 h post co-culture. Left panel: SCG cell bodies 14 days after seeding infected H358 cells in the middle compartment. Infected cells emit green fluorescence. (E) Number of fluorescence-emitting SCG cell bodies in the left compartment after overlay of neurites with MeV-RNPtracker-infected H358 cells (red dots) or after direct inoculation with MeV-RNPtracker (black triangles). Six compartmentalized cultures were seeded for each condition. Results are mean±s.e.m.
