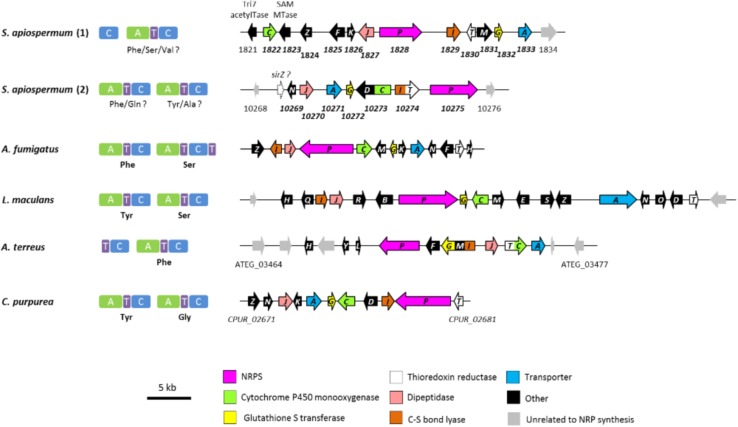
FIGURE 3.
Modular domain structure, substrate specificities and genomic organization of the different biosynthetic ETP-gene clusters. Shown are the ETP gene clusters in S. apiospermum in comparison to the gliotoxin, sirodesmin, acetylaranotin and thioclapurine clusters from A. fumigatus, L. maculans, A. terreus, and C. purpurea, respectively. Orientation of the arrows indicates the direction of transcription. Common ETP moiety genes present in all six clusters are identically colored. The “other” category contains genes encoding a zinc finger transcription factor (gliZ, sirZ, tcpZ), cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (gliF, ataF, sirB, sirE), prenyltransferases (sirD, tcpD), acetyltransferases (gliH, sirH, ataH), epimerases (sirQ, sirR, sirS), glutamyltransferases (gliK, tcpK), methyltransferases (gliM, gliN, sirM, sirN, ataM, tcpN), an oxidoreductase (sirO), a benzoate p-hydroxylase (ataY), and a hypothetical protein (ataL). Abbreviations: SAM MTase, S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyltransferase; Tri7 acetylTase, trichothecene 4-O-acetyltransferase.