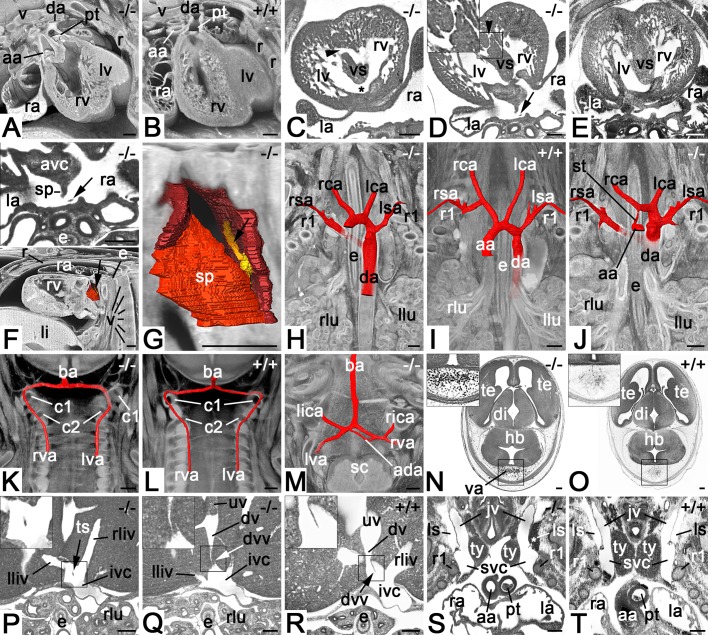
Fig. 2.
Cardiovascular malformations in Col4a2em1(IMPC)Wtsi mutant mice. (A) Double-outlet right ventricle. Axially sectioned volume models from cranio-ventral. Dorsal on top. (B) Control. (C) Combined perimembranous (asterisk) and large muscular (arrowhead) ventricular septal defects. Axial HREM section from cranial. Ventral on top. (D) Small muscular ventricular septal defect (arrowhead). Axial HREM section from cranial. Ventral on top. Note the tissue strand (arrow) in the dorsal atrium. (E) Control. (F) Abnormal tissue strand (arrow) connecting septum secundum and dorsal atrium wall. Surface models of dorsal atrium, septum primum and septum secundum (all in red) together with a sagittally and axially sectioned volume model of the thorax from lateral. Ventral to the left. Top panel (magnification of D) shows a section through the tissue strand. (G) Magnified surface model of F. Note the model of the tissue strand (yellow, arrow). (H–J) Malformations of the great intrathoracic arteries. Surface models of arteries (red) combined with coronally sectioned volume models of the cranial thorax from ventral featuring a retroesophageal right subclavian artery (H), normal situs (I) and combined stenosis of ascending aorta and retroesophageal right subclavian artery (J). (K) Abnormal topology of left vertebral artery. Surface models of vertebral and basilar arteries combined with coronally sectioned volume model of the neck from ventral. Note that the left vertebral artery enters the spinal canal below the arcus of the atlas instead of above. (L) Control. (M) Additional anastomosis between intracranial segments of left and right vertebral arteries. Surface models of arteries combined with an axially sectioned volume model of the spino-cranial junction. (N) Abnormal intracranial blood vessels dorsal to the hindbrain. Axial HREM section. Ventral on top. (O) Control. (P–R) Axial HREM sections through cranial liver segments and inferior vena cava. Tissue strand crossing junction of liver veins and vena cava inferior (P). Abnormal valve of ductus venosus (Q). Control (R). (S) Blood in left lymph sac (asterisk). Coronal resection through HREM data showing the cranial thorax and neck from ventral. Note the distance between the thymus lobes. (T) Control. Abbreviations: aa, ascending aorta; ada, additional anastomosis; avc, atriovetricular cushion; ba, basilar artery; c1, arcus of atlas; c2, arcus of axis; da, descending aorta; di; diencephalon; dv, ductus venosus; dvv, valve of ductus venosus; e, esophagus; hb, hindbrain; ivc, inferior vena cava; jv, jugular vein; la, left atrium; lca, left common carotid artery; li, liver; lica, left inferior cerebellar artery; lliv, vein from left liver lobe; llu, left lung; ls, lymph sac; lsa, left subclavian artery; lv, left ventricle; lva, left vertebral artery; pt, pulmonary trunk; r, rib; ra, right atrium; rca, right common carotid artery; rica, right inferior celebellar artery; rliv, vein from right liver lobe; rlu, righ lung; rsa, right subclavian artery; rv, right ventricle; rva, right vertebral artery; sc, spinal chord; sp, septum primum; st, aortic stenosis; svc, superior vena cava; te, telencephalon; ts, tissue strand; ty, thymus; uv, umbilical vein; v, vertebra; va, abnormal blood vessels. Scale bars: 200 µm.