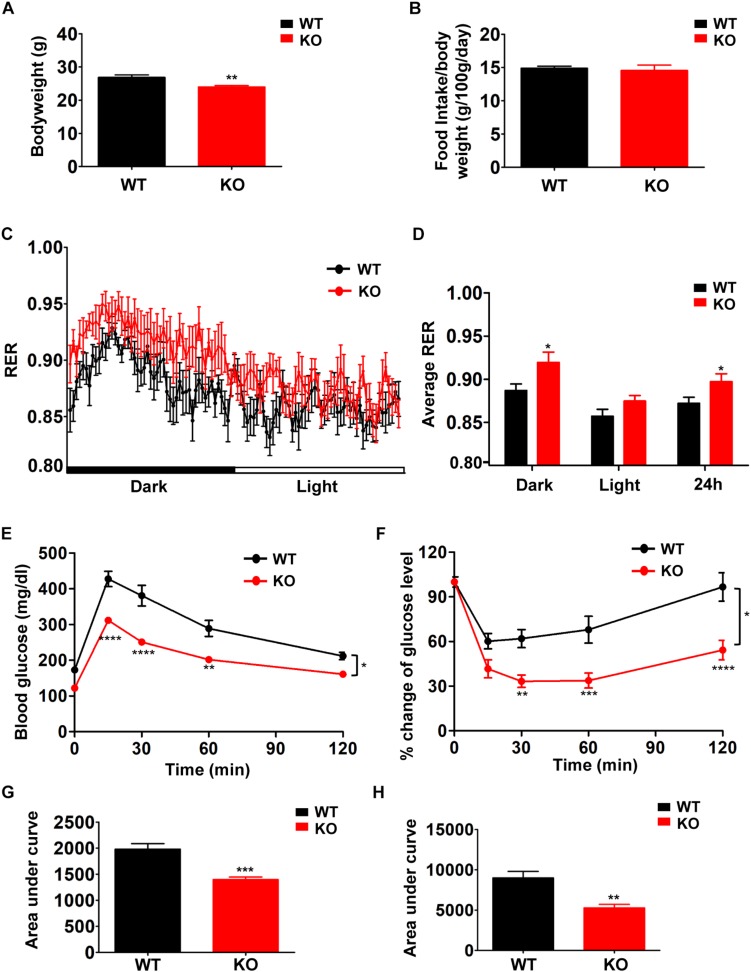
FIGURE 1.
Branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) catabolic defect reduces body weight with beneficial effects on glucose metabolism in PP2Cm KO mice. Body weight (A, n = 10–11), food intake (B, n = 10–11), respiratory exchange ratios (RER) (C, n = 9/genotype), average RER during light and dark cycles (D, n = 9/genotype), glucose tolerance test (E,G) and insulin tolerance test (F,H) of WT and PP2Cm KO male mice fed a normal diet (n = 8 for each group). Data are represented as means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared to WT.