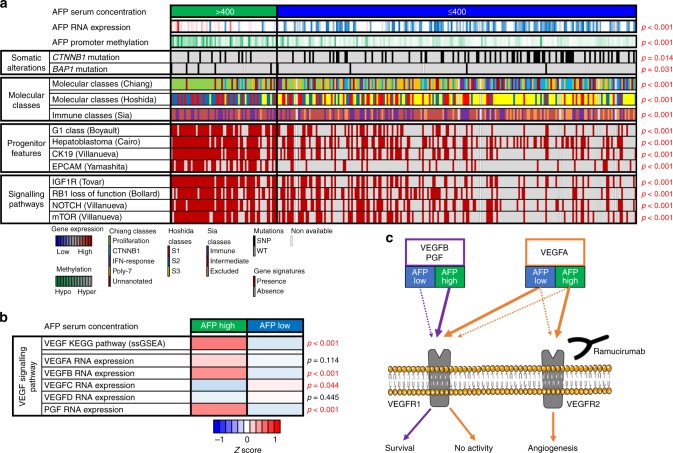
Fig. 1.
AFP-high HCCs show a distinct molecular profile. a Heatmap representation of the most relevant molecular features of AFP-high tumours (> 400 ng/ml) in comparison with AFP-low tumours in the TCGA cohort. AFP-high HCCs show higher AFP RNA expression and AFP promoter (TSS1500) hypomethylation. In terms of somatic alterations, AFP-high tumours are associated with less CTNNB1 mutations and a higher rate of BAP1 mutations. High AFP tumours are predicted to belong to the proliferation (Chiang) and S2 (Hoshida) classes and show a significant enrichment of signatures of HCC with progenitor features (G1 Boyault, Hepatoblastoma Cairo, CK19 Villanueva and EPCAM Yamashita). Finally, AFP-high tumours do not present the immune-excluded phenotype (Sia) and present overexpression of HCC signalling pathways (IGF1R Tovar, RB1 loss-of-function Bollard, NOTCH Villanueva and mTOR Villanueva). Continuous variables (AFP RNA expression and AFP promoter methylation) and categorical variables (the rest) were analysed by T test and Fisher’s exact test, respectively. b Heatmap representation of the VEGF KEGG pathway activation (inferred by single sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis) and VEGF ligands RNA expression according to AFP serum concentration in the TCGA cohort. AFP-high tumours show higher enrichment of VEGF signalling and overexpression of VEGFB and PGF. The mean values of each phenotype (AFP high and low) have been normalised and represented as a Z score. c Schematic representation of the VEGF pathway in HCC according to AFP serum concentration. The overexpression of VEGFB and PGF ligands observed in AFP-high tumours might result in an enhanced activation of VEGFR1, and at the same time, prevent VEGFA from binding VEGFR1. The competition of VEGFA with the other ligands could favour its binding to VEGFR2, ultimately leading to its subsequent activation and release of pro-angiogenic signals. The administration of ramucirumab (a monoclonal antibody against VEGFR2) might misbalance VEGFA signalling towards a preferential binding of VEGFR1, where it has limited biological activity. Purple and orange lines represent VEGFB/PGF and VEGFA signalling, respectively