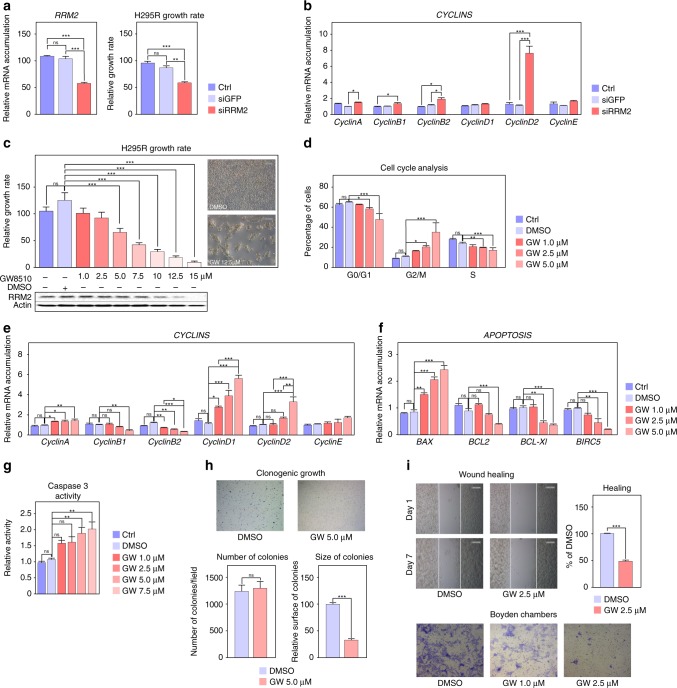
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of RRM2 reduces H295R cells growth and aggressiveness. a Effect of siRNA-mediated knockdown of RRM2 on RRM2 expression (left panel) and H295R cells growth after five days. b Effect of siRNA-mediated knockdown of RRM2 on expression of Cyclin coding genes in H295R cells was evaluated by RTqPCR. c Effect of pharmacological inhibition of RRM2 on the growth of H295R cells was determined by counting live cells after 5 days of treatment with increasing amounts of GW8510. Bottom panel shows RRM2 accumulation following GW8510 treatment. Representative images were taken at the end of treatment. d Effect of pharmacological inhibition of RRM2 on H295R cell cycle was determined by FACS following propidium iodide incorporation after 2 days of treatment with increasing amounts of GW8510. e Effect of RRM2 inhibition on expression of Cyclin coding genes in H295R cells was evaluated by RTqPCR. f Effect of RRM2 inhibition on expression of apoptosis-related genes in H295R cells was evaluated by RTqPCR. g Caspase 3 activity in H295R cells was determined after 1 day of GW8510 treatment at increasing concentrations. h Effect of RRM2 inhibition on clonogenic cell growth was determined by growing H295R cells in soft agar for 21 days in the presence or absence of 5 µM GW8510. Number and sizes of colonies were determined using Image J. i Effect of RRM2 inhibition on cell migration was determined by wound healing assays (top panel) in the absence or presence of 2.5 µM GW8510 for 7 days. For Boyden chambers migration assays (bottom panel) cells were incubated for 48h with two doses of GW8510 and migrating cells were stained with Haematoxylin. Graphs in a–g represent the mean of four experiments ± SEM. Statistical significance in these panels was evaluated by ANOVA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Graphs in h, i represent the mean of three experiments ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by Wilcoxon’s test