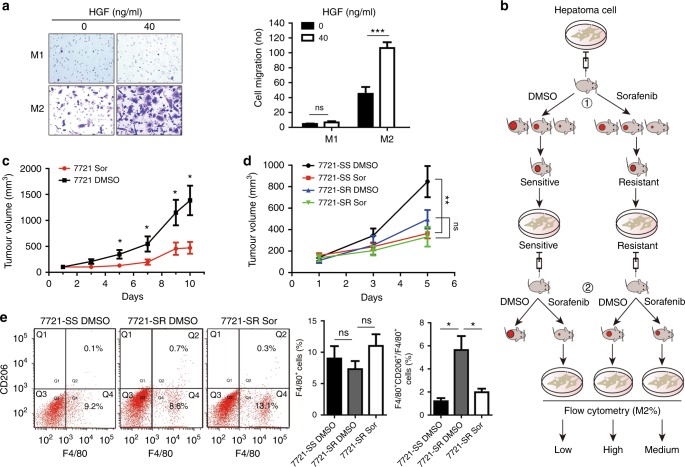
Fig. 6.
HGF chemoattracts the migration of tumour-associated M2 macrophages accumulated in sorafenib-resistant tumours. a HGF chemoattracts the migration of M2 macrophage but not M1 macrophage as determined by transwell migration assays. b Experimental procedures for development of sorafenib-resistant xenograft models by passage of HCC cells in nude mice, inducible treatment of mice with sorafenib, and implantation of mouse-passaged tumour cells in mice again. c Daily sorafenib treatment inhibited hepatoma growth in immunocompromised mice for the first round of xenograft. N = 5–6, Mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05. Tumour growth in individual mouse was shown in Supplementary Fig. 2a. d Daily sorafenib treatment of the mice greatly inhibited the tumour growth on sorafenib-sensitive (SS) tumour models (SS-Sor versus SS-DMSO, P < 0.01) but marginally affected the tumour growth on sorafenib-resistant (SR) tumour models (SR-Sor versus SR-DMSO, P > 0.05). N = 5–7, mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01, NS, no significance. e Flow cytometry assays showing SR-DMSO tumour contains more F4/80+ and CD206+ double positive M2 macrophages than that of SR-Sor tumour [SR-DMSO (N = 3) versus SR-Sor (N = 4), P < 0.05] or SS-DMSO tumour [SR-DMSO (N = 3) versus SS-DMSO (N = 3), P < 0.05)]. Mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, NS, no significance