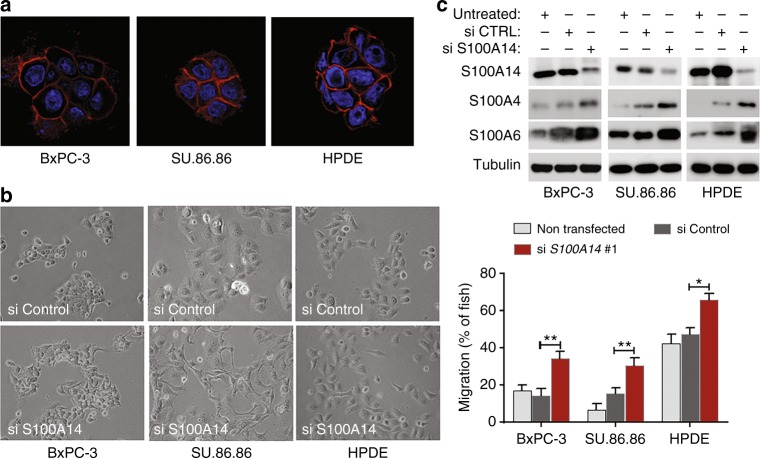
Fig. 2.
S100A14 sustains epithelial morphology and suppresses cell invasion. a Subcellular localisation of S100A14 was examined in BxPC-3 and SU.86.86 epithelial PDAC cell lines, and in human pancreatic duct epithelial (HPDE) cells by immunofluorescence. Nuclei are stained in blue (DAPI). b Phase-contrast images of PDAC epithelial cells transfected with S100A14-targeting or control siRNAs. S100A14 knockdown results in cell scattering. c Depletion of S100A14 stimulates invasion of epithelial PDAC cells in zebrafish embryos. Bars represent means (n = 3 biological replicates; 10 fish in each experiment)+/− StDev. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-Test). Western blots illustrate the degree of S100A14 depletion. Knockdown of S100A14 enhances expression levels of mesenchymal S100 proteins, but not canonical EMT markers, E-cadherin and vimentin (data not shown)