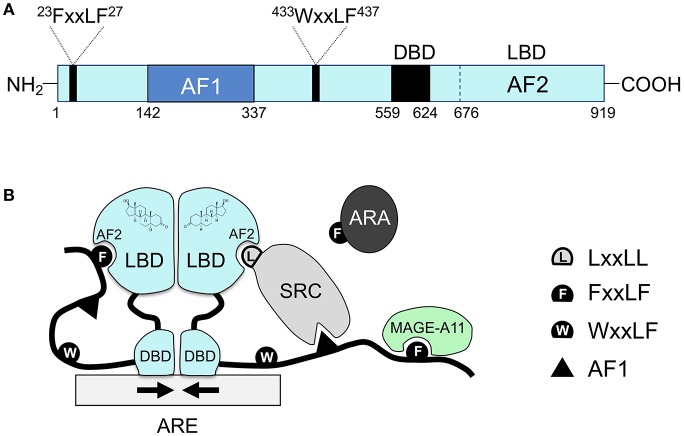
Figure 1.
The unique molecular features of the androgen receptor and its coregulator recruitment. (A) The primary sequence of the androgen receptor contains several functional domains: NH2-terminal Activation Function 1 (AF1), the central DBD, the carboxyl-terminal LBD, and two AR-specific FxxLF and WxxLF motifs. (B) Schematic diagram of homodimeric androgen receptor bound to a palindromic androgen response element (ARE). Dimerization of the androgen receptor is mediated by both DBD and LBD. Shown in the diagram are FxxLF motif-mediated N/C interaction, recruitment of the SRC/p160 by AF1 and AF2, recruitment of FxxLF motif-containing ARA proteins by AF2, and recruitment of MAGE-A11 through the AR NH2-terminal extended FxxLF motif. Competition likely exists among different FxxLF, WxxLF, and LxxLF motifs for binding to the same AF2 site on AR LBD (1). SRC, steroid receptor coactivator; ARA, AR-associated protein; AF1, activation function 1; AF2, activation function 2, a hydrophobic cleft in the LBD; ARE, androgen response element; DBD, DNA binding domain; LBD, ligand binding domain.