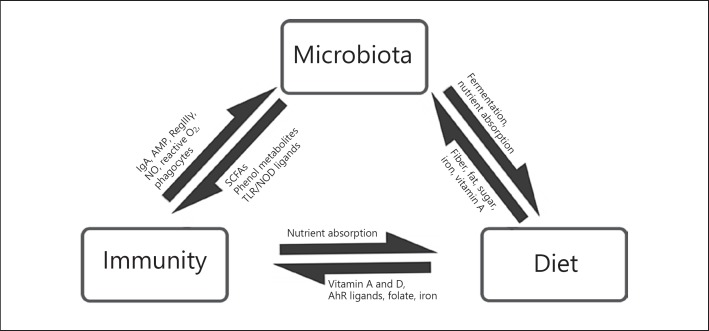
Fig. 1.
Bidirectional interactions between microbiota, immunity, and diet (adapted from Belkaid and Hand [4]). Dietary components such fiber, fat, sugars, and trace nutrients modulate microbiota composition and metabolic capacity. Microbiota help in digestion and nutrient uptake. Dietary nutrients and metabolites (such as AhR ligands) produced by microbiota modulate the immunity. The host immune system can affect the nutrient uptake. The immune system regulates microbiota by various mechanisms such as AMP, IgA, reactive oxygen species, and phagocytosis. The microbiota in turn produces metabolites that modulate the functioning of the immune system.