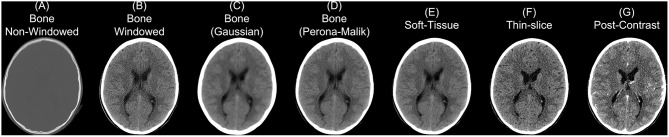
Figure 2.
Different series for a scanning study. Here we present different non-contrast head CT exported from a PACS. We display a reconstructed scan with a bone convolution kernel (A), showing bright areas of the skull, which can be investigated for breaks or fractures. When applying a window of 0–100 Hounsfield units (HU) of this image, we see the image resolution (B). Using a Gaussian (C) or Perona-Malik (D) smoother, we see the resulting image smoothness is similar to the image reconstructed with a soft-tissue convolution kernel (E). Images (A–E) had a slice thickness of 5 mm. The thin-slice scan (F) had a slice thickness of 0.62 mm and a soft-tissue convolution kernel. CT scan with contrast agent (G) to show how the contrast affects the CT image.