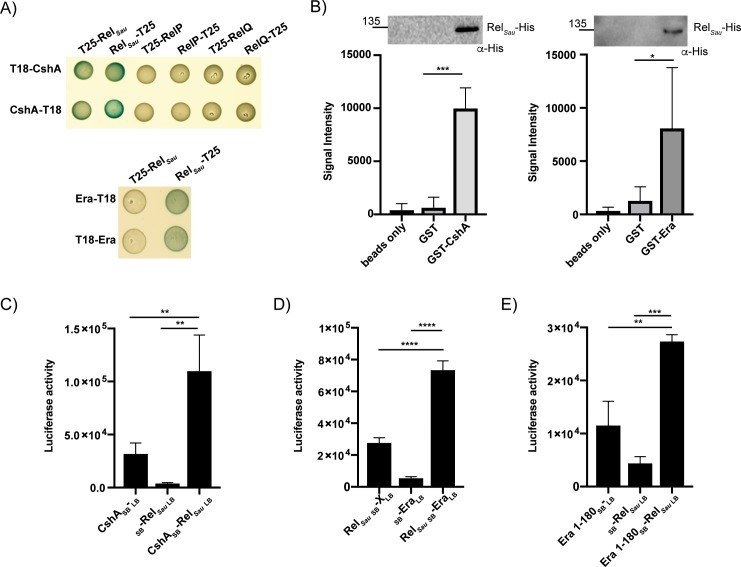
Fig 5. The stringent response synthetase RelSau interacts with Era and CshA.
A) Top: Bacterial two-hybrid showing an interaction between CshA-T18/T18-CshA and both RelSau-T25 and T25-RelSau. CshA did not interact with the small (p)ppGpp synthetase enzymes RelP or RelQ. Bottom: Bacterial two-hybrid showing an interaction between RelSau-T25 and both Era-T18 and T18-Era. N = 3 with one representative image shown. B) Affinity pulldown assay using GST, GST-tagged CshA and GST-tagged Era coupled to glutathione beads. Beads alone, GST, GST-Era or GST-CshA coupled beads were incubated with His-tagged RelSau. After washing, bound RelSau-His was detected using HRP-conjugated anti-His antibodies. N = 3 or 4 with one representative image shown above. Below, the mean signal intensities and standard deviations from the repeats are plotted. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (* P < 0.05, *** P < 0.0005). C, D & E) Split luciferase assays demonstrating an interaction between CshA (C), Era (D) or Era 1–180 (E) and RelSau in S. aureus. The negative controls have genes singly fused to either SB or LB. The average values and standard deviations of triplicate experiments (N = 3) are plotted. All statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (** P < 0.005, *** P < 0.0005, **** P < 0.0001).