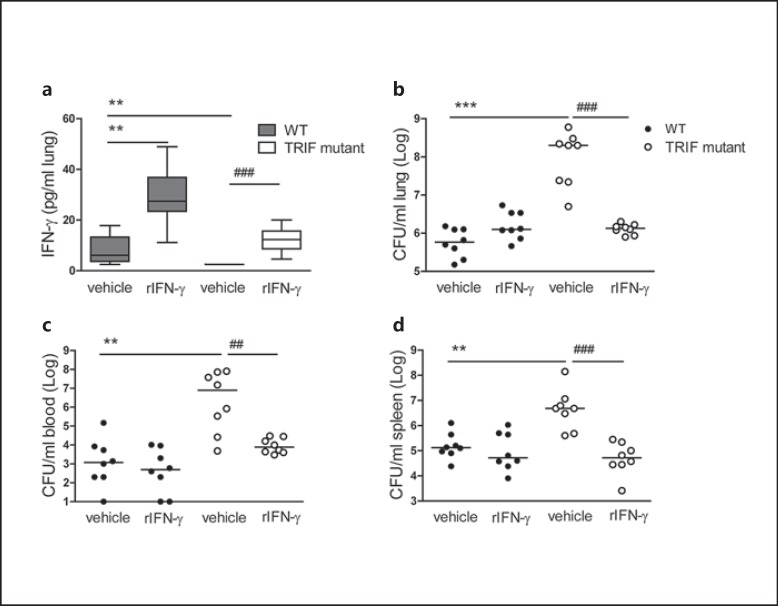
Fig. 3.
Administration of rIFN-γ via the airways restores antibacterial defense in TRIF mutant mice. WT and TRIF mutant mice were infected with about 104 CFU K. pneumonia; 50 ng recombinant IFN-γ or vehicle was administered intranasally 30 min before infection and 24 h afterwards (n = 8 mice each group). Mice were sacrificed after 48 h of infection. IFN-γ levels in lung homogenates 48 h after infection (a) are expressed as box-and-whisker diagrams depicting the smallest observation, lower quartile, median, upper quartile and largest observation. Bacterial loads are shown in the lung (b), blood (c) and spleen (d) 48 h after infection. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, horizontal lines represent medians. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. WT mice treated with vehicle, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. TRIF mutant mice treated with vehicle, Mann-Whitney U test, and Fisher exact test was used for comparison between TRIF mutant groups (performed post hoc after Kruskal-Wallis test).