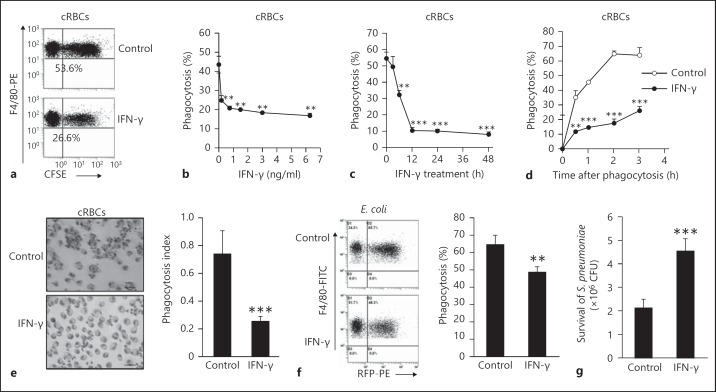
Fig. 1.
IFN-γ significantly inhibited the nonopsonized phagocytosis of macrophages. The F4/80+ PEMs isolated from C57BL/6 mice were subjected to phagocytic nonopsonized CFSE-cRBCs (5 × 106) in the presence or absence of IFN-γ (1 ng/ml), and were then stained with PE-conjugated anti-F4/80 mAb (BM8). After three washes with FCM buffer, phagocytosis (%) of F4/80+ cells was determined by FCM. a One representative FCM displays gated F4/80+ cells. b, c IFN-γ inhibited the nonopsonized phagocytosis of macrophages in a dose- (b) and time-dependent manner (c). d IFN-γ inhibited the nonopsonized phagocytosis of macrophages even after prolonged phagocytosis as determined by FCM. e IFN-γ inhibited the nonopsonized phagocytosis of macrophages as determined under a microscope. ×40. f The freshly isolated F4/80+ PEMs were cocultured with CFSE-labeled E. coli (5 × 107) in the presence or absence of IFN-γ, and then phagocytosis (%) of F4/80+ cells was determined by FCM. g Survival of S. pneumoniae after coculture with IFN-γ-treated and control macrophages. Data are the mean ± SD (n = 3–5/group) from one of at least two independent experiments with identical results. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001, vs. the control group or the indicated group. PE = Phycoerythrin; RFP = red fluorecent protein.