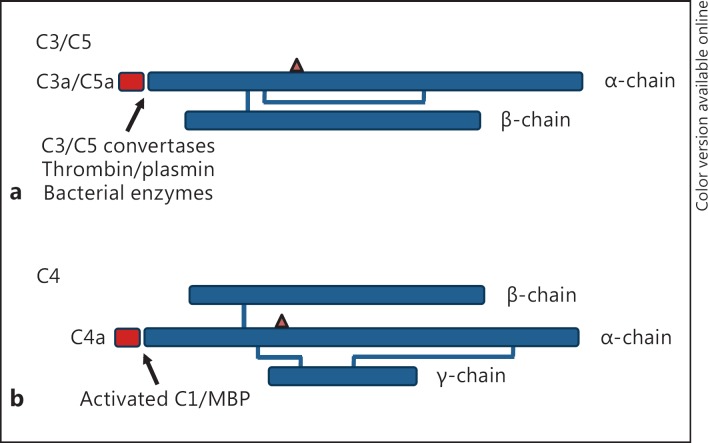
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the polypeptide structure of human C3, C4, and C5. a C3 and C5 are composed of an α- and a β-chain that have inter- and intrachain disulfide bridges. C3a and C5a are derived by cleavage of the amino-terminal end of the α-chain by C3/C5 convertases, activated coagulation proteases including thrombin, plasmin, and factors IX through XI, and by bacterial enzymes. b C4 is composed of 3 polypeptide chains (α, β, and γ) which also have inter- and intrachain disulfide bridges. C4a is derived by cleavage of the amino-terminal end of the α-chain by activated C1 on activation of the classical, or by activated mannose binding protein on activation of the lectin pathway. The triangle indicates the relative position of the thioester bond found in the α-chain of C3 and C4.