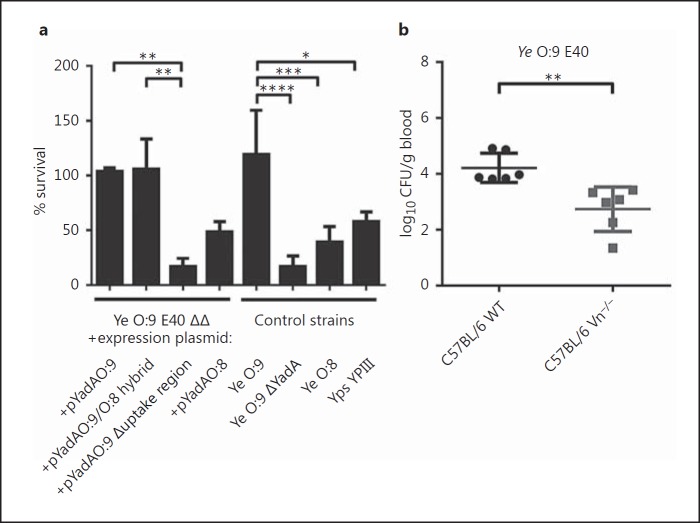
Fig. 7.
Ye O:9 E40 is resistant to complement-mediated killing in vitro, and in an in vivo serum killing assay, Ye is more efficiently eliminated in the absence of Vn. a An in vitro serum killing assay using Ye O:9 E40, Ye O:9 E40 ΔYadA, Ye O:8 WA-314, Yps YPII, Ye O:9 E40 ΔΔ + pASK-IBA4C_yadAO:8, Ye O:9 E40 ΔΔ + pASK-IBA4C_yadAO:9, Ye O:9 E40 ΔΔ + pASK-IBA4C_yadAO:9/O:8 hybrid, Ye O:9 E40 ΔΔ + pASK-IBA4C_yadAO:9 Δuptake region. The serum bactericidal effect was calculated as the survival percentage. b WT and Vn−/− mice were infected intravenously with 1 × 107Ye O:9 E40 for 30 min. After that, the mice were killed, and blood was withdrawn and plated on selective agar plates. CFU were determined by counting colonies the next day, shown as log10 CFU per gram of blood. a Data are means ± SD of at least 3 individual experiments. The main p value was determined by one-way ANOVA (p < 0.0001). Multiple comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparisons test. b The p value for the comparison of C57BL/6 and Vn−/− mice was determined by Student's t test. The horizontal lines denote the mean and the error bars denote the SD. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p > 0.0001 (n = 6).