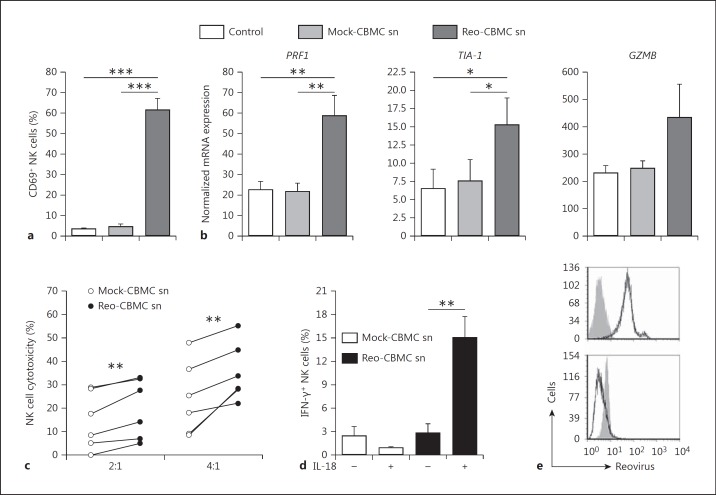
Fig. 1.
Soluble mediator(s) produced by reovirus-infected mast cells activate NK cells. Purified peripheral blood human NK cells were cultured in Mock-CBMC sn, Reo-CBMC sn or culture medium (Control) for 24 h. a A purified lymphocyte population (≥90% CD3−CD56+ cells) was analyzed for CD69 expression by FACS (n = 7). bPRF1 (n = 6), TIA-1 (n = 5) and GZMB (n = 5) gene expression was analyzed by qPCR and shown as normalized to GAPDH. c NK cells were resuspended in either Mock-CBMC sn or Reo-CBMC sn and cytotoxic activity against the K562 cell line was analyzed by LDH release assay at ratios of 2:1 and 4:1 (E:T) after 4 h of coculture (n = 6). All conditions were carried out in triplicate. d IFN-γ production was determined following stimulation with either Mock-CBMC sn or Reo-CBMC sn in the presence (+) or absence (-) of 100 ng/ml IL-18 (n = 7). Samples were analyzed by FACS. Data were compared using repeated-measures ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test (a, b) or paired t test (c, d). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Results are presented as mean ± SEM from at least 3 independent experiments performed on at least 5 different donors. e Reovirus infection was analyzed by FACS in CBMC (upper panel, n = 6) and NK cells (lower panel, n = 2) after culture with 20 MOI reovirus or Reo-CBMC sn, respectively. Isotype control (filled histograms) and anti-reovirus (empty histograms and black line) are shown.