FIGURE 2.
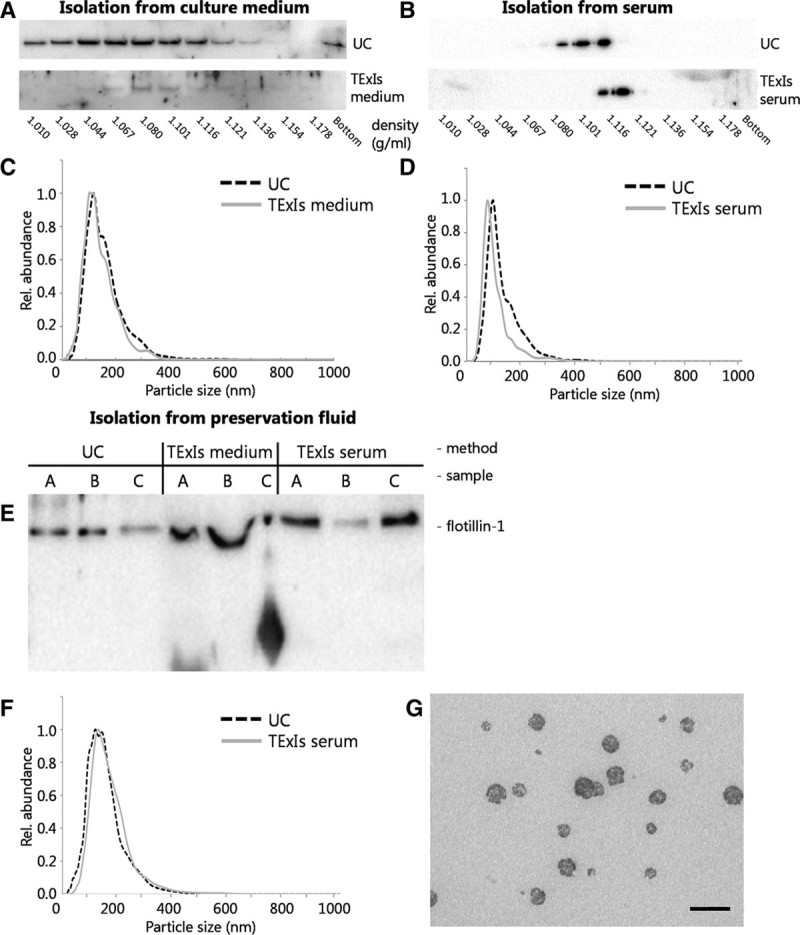
A precipitation method for perfusion fluid sEVs. sEVs were isolated from human microvascular endothelial cells-1-conditioned culture medium or human serum using sequential UC or precipitation (using the TExIs reagent for culture medium or serum, respectively) and subsequently analyzed by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation and immunoblotting for β-actin. sEVs isolated from culture medium by precipitation (A, TExIs medium) appeared slightly more dense than those isolated by ultracentrifugation (A, UC). Also, sEVs isolated from serum using the TExIs reagent for serum (B, TExIs serum) appeared slightly more dense than those isolated by ultracentrifugation. Size distribution of the sEVs from either source and by either method did not significantly differ (C,D). Immunoblotting of sEVs from 3 different donor fluids isolated by ultracentrifugation (UC) or TExIs reagents for culture media (TExIs medium) or serum (TExIs serum) show a disturbed running pattern for those isolated using the reagent for serum (E). sEVs were isolated from preservation fluid by UC or using the TExIs reagent for serum (TExIs serum). F, Subsequent NTA analysis shows that both sEV preparations contain equally sized particles, consistent with the size of small EVs. G, TEM analysis of the precipitated sEVs confirms the presence of sEVs, with signs of co-isolated reagent (scale bar = 200 nm). EVs, extracellular vesicles; NTA, nanoparticle tracking analysis; sEVs, small extracellular vesicles; TExIs, Total Exosome Isolation.
