Fig. 1. iP300w diminishes DUX4-induced toxicity.
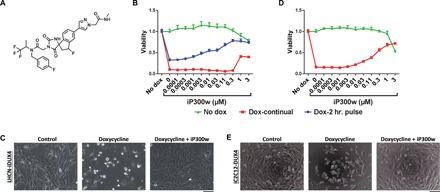
(A) Chemical structure of iP300w. (B) Cell viability assay [adenosine triphosphate (ATP) assay] on LHCN-iDUX4 myoblasts at 48 hours. Red series (Dox-continual): Cells were continually exposed to dox (200 ng/ml) for the full 48 hours and treated with serial dilutions of iP300w. Blue series (Dox-2-hr. pulse): Cells were induced for 2 hours with dox (200 ng/ml) and then washed, and medium was replaced with dox-free medium containing different concentrations of iP300w. Green series (Control): Noninduced LHCN-iDUX4 cells were treated only with different concentrations of iP300w. Data are presented as fold difference compared to the control untreated cells (n = 8). (C) Morphology of LHCN-iDUX4 cells after 48 hours with continual dox (200 ng/ml) induction and treatment with iP300w (1 μM). (D) ATP assay on iC2C12-DUX4 at 48 hours of induction with dox (500 ng/ml) and treatment with various concentrations of iP300w, as in (B). (E) Morphology of iC2C12-DUX4 cells at 48 hours of continual dox (500 ng/ml) induction and iP300w (1 μM) treatment. Concentrations of dox for both cell lines were determined to provide rapid cell death within 48 hours of induction.
