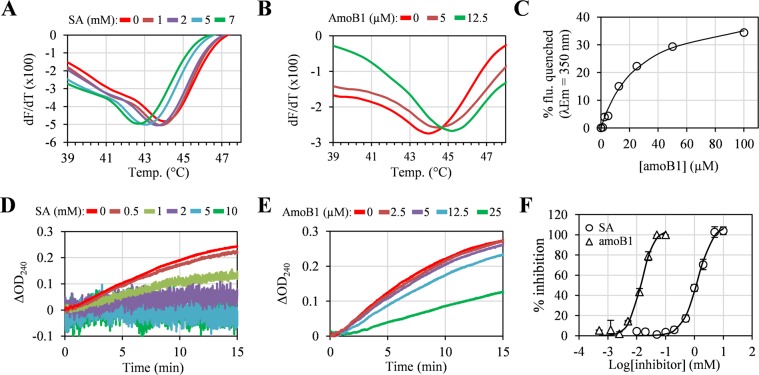
Figure 3.
Interaction and inhibition of ENO1 with SA and amorfrutin B1 (amoB1). (A,B) Thermal stability assay of ENO1 with different concentrations of SA (A) or amoB1 (B). For the thermal stability assay, different concentrations of salicylates (SA or amoB1) were incubated with 2 µM ENO1 for 30 min at RT, then melting curves were obtained by monitoring the fluorescence at 590 nm. (C) Tryptophan (Trp) intrinsic fluorescence assay of ENO1 with different concentrations of amoB1. For the Trp intrinsic fluorescence assay, different concentrations of salicylates were incubated with 1 µM ENO1 for 30 min at RT, then Trp emission fluorescence was obtained (excitation/emission = 295 nm/350 nm). (D,E) Inhibition of ENO1 enzymatic activity by SA (D) or amoB1 (E). For the inhibition assays, different concentrations of salicylates were incubated with 0.1 µM ENO1 for 30 min at RT, 2.5 mM 2-PGA was added, then the production of PEP was measured by monitoring the absorbance at 240 nm. Background signals induced by reaction solutions containing salicylates and 2-PGA, but without ENO1, were subtracted to calculate ΔOD240. (F) Percent inhibition of ENO1 activity by SA and amoB1. Percent inhibition was calculated by monitoring the ΔOD240 at 5 min with or without salicylates. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). Experiments were repeated three times with similar results.