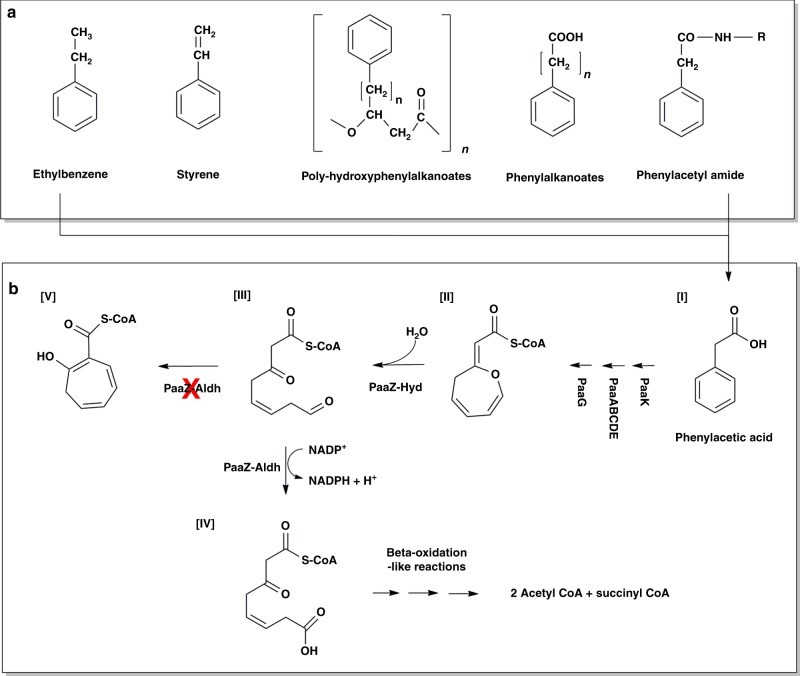
Fig. 1.
Overview of phenyl acetic acid (paa) degradation pathway. a Several environmental pollutants such as styrene, ethylbenzene and others converge to paa through peripheral pathways. b The first reaction in paa pathway is catalyzed by PaaK, which covalently links paa (I) with CoA giving rise to paa-CoA. The next reaction is catalyzed by a multi-component monooxygenase system PaaABCDE followed by isomerase PaaG to yield Oxepin CoA (II), which is the substrate for PaaZ. PaaZ-Hyd performs the hydratase reaction to yield 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA semialdehyde (III). PaaZ-Aldh domain reduces the semi-aldehyde intermediate to a ring opened 3-oxo-5,6-dehydrosuberyl-CoA (IV) which is further reduced to acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA via a reaction similar to beta-oxidation. If either PaaZ-Aldh is impaired or if the enzyme is not supplemented with NADP+, the semialdehyde intermediate (III) rapidly forms a dead end product 2-hydroxycyclohepta-1,4,6-triene-1-carboxyl-CoA (V), which cannot be rescued by the addition of functional aldehyde dehydrogenase domain. Figure based on Fuchs et al.15