Fig. 2.
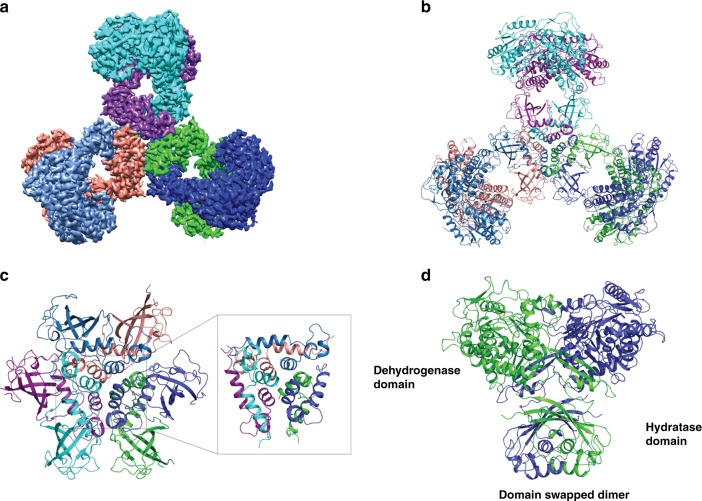
Architecture of PaaZ. a CryoEM map of substrate-free PaaZ revealing a trilobed architecture. The density corresponding to each monomer is colored individually, clearly showing the domain swap in each module. b The model derived from the cryoEM map with each polypeptide colored as in panel a. The final model consists of residues 2–679 with only the loop regions defined poorly. c Six monomers of the hydratase domain form the central inner core. Short helices from each monomer form two layers with an additional helix that lies perpendicular and wraps around to form a tight knit core (inset). d Two polypeptides of PaaZ (green and blue) form a module with the domain of the C-terminal hydratase, which is swapped between monomers