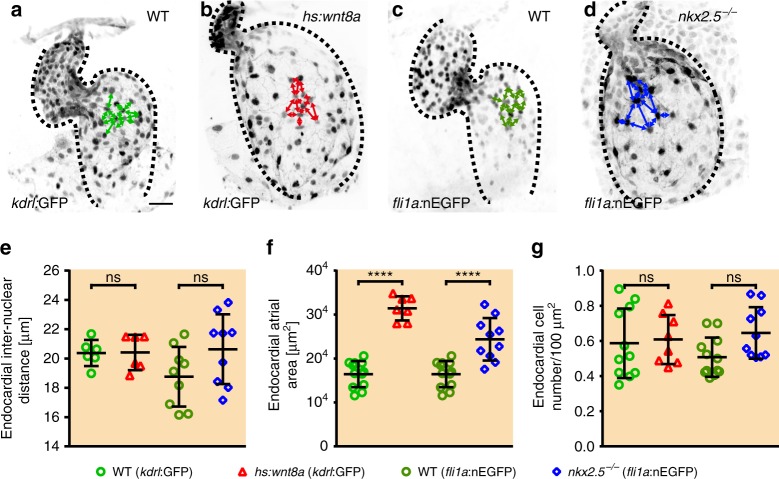
Fig. 3.
Endocardial cell sizes are not altered upon atrial chamber expansion. a–d Reconstructions of confocal z-stacks of representative hearts at 52 hpf of (a) WT, (b) upon Wnt8a overexpression, (c) WT, or (d) in nkx2.5vu179 mutants. Endocardial GFP expression of Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 or Tg(fli1a:nEGFP)y7 is inverted in black/white. Endocardial inter-nuclear distances are indicated by arrows and a dotted line indicates the outline of the endocardium. Scale bars, 30 µm. e Quantifications of endocardial inter-nuclear distances reveal no significant differences between WT (kdrl:GFP n = 6 hearts, fli1a:nEGFP n = 9 hearts), upon Wnt8a overexpression (n = 6 hearts), or in nkx2.5vu179 mutants (n = 9 hearts). Each dot represents one heart with an average of at least 20 length measurements within the endocardial atrium. f Quantifications of the atrial endocardial surface area reveals a significant increase upon Wnt8a overexpression (n = 7 hearts) or loss of Nkx2.5 (n = 10 hearts) compared to WT hearts (kdrl:GFP n = 12 hearts, fli1a:nEGFP n = 12 hearts). g Quantifications of the ratio of endocardial cell numbers relative to total atrial chamber area indicates no significant differences between WT (kdrl:GFP n = 11 hearts, fli1a:nEGFP n = 12 hearts), upon Wnt8a overexpression (n = 8 hearts), or in nkx2.5vu179 mutants (n = 10 hearts). e–g Mean values ± SD are shown. One-way ANOVA was used to compare each condition with its WT control (ns: not significant, ****p < 0.0001)