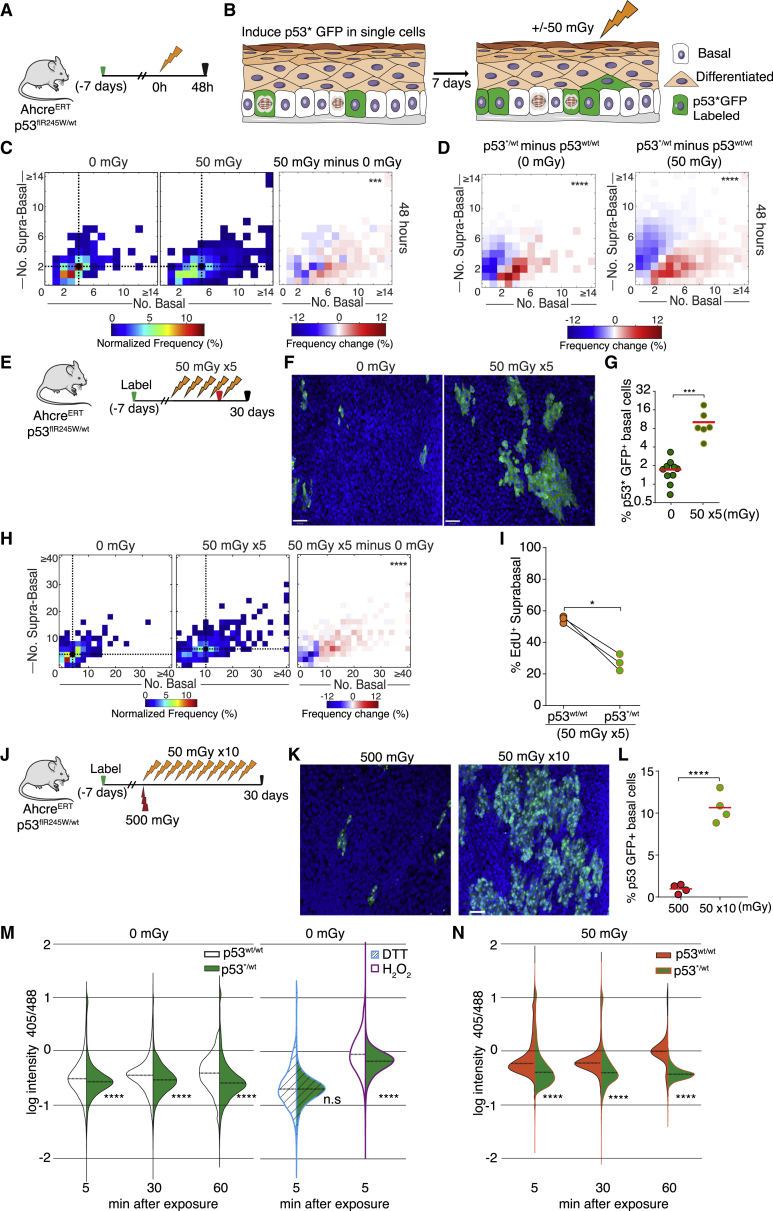
Figure 5.
The p53∗/WT Mutant Population Expands after Single Exposure or Multiple Exposures to LDIR
(A) Experimental protocol. Mice with a conditional p53R245W-GFP/WT (p53∗/WT) allele were induced (green arrow), giving p53∗ and GFP expression in single progenitor cells. 7 days later, animals were irradiated with a single exposure of 50 mGy of LDIR and culled 48 h after the last irradiation.
(B) Cartoon of lineage tracing in this protocol.
(C) Heatmaps showing the frequency of p53∗/WT clones containing the number of basal and suprabasal cells indicated (left panels) and the frequency change observed when comparing 0 and 50 mGy irradiated animals (right panel). Black dots, geometric clone-size median. ∗∗∗p = 0.0007 (Peacock’s test); n = 150 and 450, respectively.
(D) Heatmaps showing the frequency change observed when comparing p53∗/WT and p53WT/WT (wild-type) clones 48 h after exposure to 0 or 50 mGy LDIR. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Peacock’s test).
(E) Experimental protocol. Mice with a conditional p53R245W-GFP/WT (p53∗/WT) allele were induced (green arrow), giving p53∗ and GFP expression in single progenitor cells. 7 days later, animals were irradiated with five doses of 50 mGy of LDIR over 30 days, commenced with a minimal separation of 3 days between each dose. EdU was given 1 h prior to the last irradiation (red arrow), and animals were culled 48 h later.
(F) Top-down views of confocal z stacks of typical EE whole mounts showing p53∗/WT clones (green) after 0 or 50 mGy × 5 LDIR. Basal layer cells are shown (DAPI, blue). Scale bars, 28 μm.
(G) Percentage of p53∗/WT basal cells after 0 or 50 mGy × 5. Points show mean values from individual mice. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (t test); n = 7 (0 mGy) and n = 6 (50 mGy) mice.
(H) Heatmaps showing the frequency of p53∗/WT clones containing the number of basal and suprabasal cells of the indicated sizes (left panels) and the frequency change observed in 0 and 50 mGy × 5 doses irradiated animals (right panel). Black dots and dashed lines indicate geometric median clone size. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Peacock’s test), n = 300 clones per condition.
(I) Comparison of p53∗/WT clones with adjacent p53WT/WT EE in the same irradiated animal. Shown is the percentage of EdU+ suprabasal cells. Points show mean values from 3 mice, and lines link the same animal. ∗p < 0.05 (paired t test).
(J) Experimental protocol to study repeated radiation exposure. p53R245W-GFP/WT mice were induced as in (A) and (E), and 7 days later, animals were irradiated with a single dose of 500 mGy or with a course of ten doses of 50 mGy. At 30 days, both groups were analyzed for p53∗/WT clone size.
(K) Top-down views of confocal z stacks of typical EE whole mounts showing p53∗/WT clones (green) 1 month after 500 mGy or 50 mGy × 10 LDIR. Basal layer cells are shown (DAPI, blue). Scale bars, 30 μm.
(L) Percentage of p53∗/WT basal cells shown in (K). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (t test). At least 25,000 basal cells were quantified per condition. n = 4 mice per condition.
(M) and (N) Primary keratinocyte 3D cultures from p53WT/WT and p53∗/WT EE were infected with an adenovirus encoding a genetic sensor of the mitochondrial redox state and irradiated, and single mitochondria were imaged by confocal microscopy. Violin plots show the distribution of 405/488 ratios for individual mitochondria in Mito-Grx1-roGFP2 reporter-expressing keratinocytes from p53WT/WT (white in M; orange in N) and p53∗/WT (green) 5, 30, and 60 min after 0 mGy (M) or 50 mGy LDIR (N), obtained by quantitative confocal 3D imaging. Controls are oxidized (H2O2-treated) and reduced (DTT-treated) cells for each strain. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Mann-Whitney U test). The numbers of mitochondria imaged under each condition are shown in Table S1. Three biological replicate experiments were performed; results from a representative experiment are shown.
See also Figures S1 and S5 and Tables S2 and S4.