Figure 1.
CTIP2KO MSNs Acquire Normal Striatal Cell Identity but Present with Increased Vulnerability to Oxidative Stress
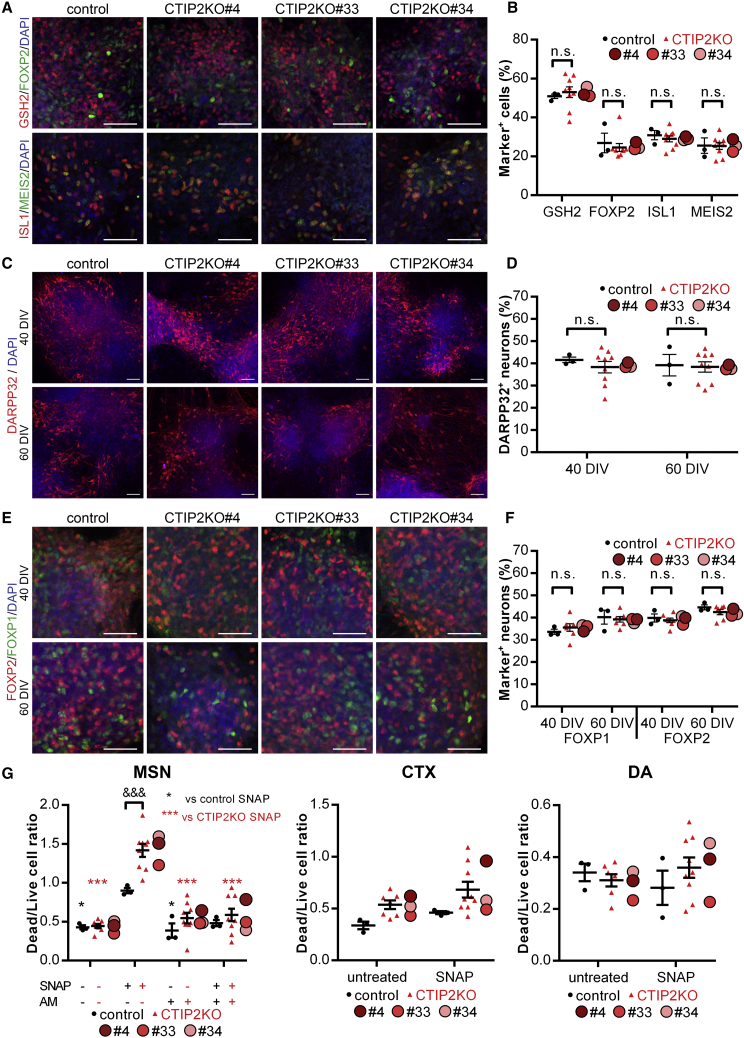
(A and B) LGE-like progenitors in control and CTIP2KO cultures at 20 DIV labeled and quantified for GSH2, FOXP2, ISL1, and MEIS2 (n = 3, 9, 3).
(C and D) MSNs in control and CTIP2KO cultures at 40 and 60 DIV labeled and quantified for DARPP32 (n = 3, 9, 3).
(E and F) MSNs in control and CTIP2KO cultures at 40 and 60 DIV labeled and quantified for FOXP1 and FOXP2 (n = 3, 7, ≥2).
(G) Pre-treatment of MSNs with 50 μM amentoflavone (AF) for 2 h protects them from SNAP-induced cell death at 40 DIV. Similar vulnerability to oxidative stress is observed between control and CTIP2-deficient groups in both cortical neurons (CTX) and dopaminergic (DA) neurons (n = 3, 9, 3).
(A, C, and E) Scale bars, 50 μm. (B, D, and F) One-way ANOVA; n.s., not significant. (G) Two-way ANOVA; MSN: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; &&&p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SEM for each genotype, with the means for individual clones indicated by red-shaded circles beside CTIP2KO data.
See also Figures S1 and S2.